Table of Contents
Can You Drink Tap Water in Mcallen?
Yes, Mcallen's tap water is generally considered safe to drink as Mcallen has no active health based violations of the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) that we are aware of. Other factors such as lead piping in a home, or low levels of pollutants on immunocompromised individuals, should also be considered, however. To find more recent info we might have, you can check out our boil water notice page, the city's water provider website, or Mcallen's local Twitter account.
According the EPA’s ECHO database, from April 30, 2019 to June 30, 2022, Mcallen's water utility, Mcallen Public Utility, had 0 violations of the Safe Drinking Water Act. For more details on the violations, please see our violation history section below. The last violation for Mcallen was resolved on May 31, 2018. This assessment is based on the Mcallen Public Utility water system, other water systems in the city may have different results.
While tap water that meets the EPA health guidelines generally won’t make you sick to your stomach, it can still contain regulated and unregulated contaminants present in trace amounts that could potentially cause health issues over the long-run. These trace contaminants may also impact immunocompromised and vulnerable individuals.
The EPA is reviewing if it’s current regulations around pollutant levels in tap water are strict enough, and the health dangers posed by unregulated pollutants, like PFAS.
Water Quality Report for Mcallen Tap Water
The most recent publicly available numbers for measured contaminant levels in Mcallen tap water are in its 2020 Water Quality Report. As you can see, there are levels which the EPA considers to be acceptable, but being below the maximum allowable level doesn’t necessarily mean the water is healthy.
Lead in tap water, for example, is currently allowed at up to 15ppb by the EPA, but it has set the ideal goal for lead at zero. This highlights how meeting EPA standards doesn’t necessarily mean local tap water is healthy.
EPA regulations continue to change as it evaluates the long term impacts of chemicals and updates drinking water acceptable levels. The rules around arsenic, as well as, lead and copper are currently being re-evaluated.
There are also a number of "emerging" contaminants that are not currently. For example, PFAS (Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), for which the EPA has issued a health advisory. PFAS are called "forever chemicals" since they tend not to break down in the environment or the human body and can accumulate over time.
We recommend looking at the contaminants present in Mcallen's water quality reports, or getting your home's tap water tested to see if you should be filtering your water.
Mcallen Tap Water Safe Drinking Water Act Violation History - Prior 10 Years
Below is a ten year history of violations for the water system named Mcallen Public Utility for Mcallen in Texas. For more details please see the "What do these Violations Mean?" section below.
From May 1, 2018 to May 31, 2018, Mcallen had 1 non-health based Safe Drinking Water Act violation with the violation category being Monitoring and Reporting, more specifically, the violation code was Monitoring and Reporting (DBP) which falls into the Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule rule code group, and the Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule rule code family for the following contaminant code: Chlorite.
From April 1, 2012 to April 30, 2012, Mcallen had 1 non-health based Safe Drinking Water Act violation with the violation category being Monitoring and Reporting, more specifically, the violation code was Monitoring and Reporting (DBP) which falls into the Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule rule code group, and the Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule rule code family for the following contaminant code: Chlorite.
Is there Lead in Mcallen Water?
Based on the EPA’s ECHO Database, 90% of the samples taken from the Mcallen water system, Mcallen Public Utility, between sample start date and sample end date, were at or below, 0.0007 mg/L of lead in Mcallen water. This is 4.7% of the 0.015 mg/L action level. This means 10% of the samples taken from Mcallen contained more lead.
While Mcallen water testing may have found 0.0007 mg/L of lead in its water, that does not mean your water source has the same amount. The amount of lead in water in a city can vary greatly from neighborhood to neighborhood, or even building to building. Many buildings, particularly older ones, have lead pipes or service lines which can be a source of contamination. To find out if your home has lead, we recommend getting you water tested.
No amount of lead in water is healthy, only less dangerous. As lead accumulates in our bodies over time, even exposure to relatively small amounts can have negative health effects. For more information, please check out our Lead FAQ page.
Are there PFAS in Mcallen Tap Water?
Currently, testing tap water for PFAS isn’t mandated on a national level. We do have a list of military bases where there have been suspected or confirmed leaks. There appears to be no military bases near Mcallen with suspected leaks.
With many potential sources of PFAS in tap water across the US, the best information we currently have about which cities have PFAS in their water is this ewg map, which you can check to see if Mcallen has been evaluated for yet.
Our stance is better safe than sorry, and that it makes sense to try to purify the tap water just in case.
Mcallen SDWA Violation History Table - Prior 10 Years
| Compliance Period | Status | Health-Based? | Category Code | Code | Rule Code | Contaminant Code | Rule Group Code | Rule Family Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05/01/2018 - 05/31/2018 | Resolved | No | Monitoring and Reporting (MR) | Monitoring and Reporting (DBP) (27) | Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule (210) | Chlorite (1009) | Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule (200) | Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule (210) |
| 04/01/2012 - 04/30/2012 | Resolved | No | Monitoring and Reporting (MR) | Monitoring and Reporting (DBP) (27) | Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule (210) | Chlorite (1009) | Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule (200) | Stage 1 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule (210) |
What do these Violations Mean?
Safe Drinking Water Act Violations categories split into two groups, health based, and non-health based. Generally, health based violations are more serious, though non-health based violations can also be cause for concern.
Health Based Violations
- Maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) - maximum allowed contaminant level was exceeded.
- Maximum residual disinfectant levels (MRDLs) - maximum allowed disinfectant level was exceeded.
- Other violations (Other) - the exact required process to reduce the amounts of contaminants in drinking water was not followed.
Non-Health Based Violations
- Monitoring and reporting violations (MR, MON) - failure to conduct the required regular monitoring of drinking water quality, and/or to submit monitoring results on time.
- Public notice violations (Other) - failure to immediately alert consumers if there is a serious problem with their drinking water that may pose a risk to public health.
- Other violations (Other) - miscellaneous violations, such as failure to issue annual consumer confidence reports or maintain required records.
SDWA Table Key
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Compliance Period | Dates of the compliance period. |
| Status |
Current status of the violation.
|
| Health-Based? | Whether the violation is health based. |
| Category Code |
The category of violation that is reported.
|
| Code | A full description of violation codes can be accessed in the SDWA_REF_CODE_VALUES (CSV) table. |
| Contaminant Code | A code value that represents a contaminant for which a public water system has incurred a violation of a primary drinking water regulation. |
| Rule Code |
Code for a National Drinking Water rule.
|
| Rule Group Code |
Code that uniquely identifies a rule group.
|
| Rule Family Code |
Code for rule family.
|
For more clarification please visit the EPA's data dictionary.
Mcallen Water - Frequently Asked Questions
| By Mail: | PO BOX 220 MCALLEN, TX, 78505-0220 |
Existing customers can login to their Mcallen Public Utility account to pay their Mcallen water bill by clicking here.
If you want to pay your Mcallen Public Utility bill online and haven't made an account yet, you can create an account online. Please click here to create your account to pay your Mcallen water bill.
If you don't want to make an account, or can't remember your account, you can make a one-time payment towards your Mcallen water bill without creating an account using a one time payment portal with your account number and credit or debit card. Click here to make a one time payment.
Moving to a new house or apartment in Mcallen means you will often need to put the water in your name with Mcallen Public Utility. In order to put the water in your name, please click the link to the start service form below. Start service requests for water bills typically take two business days.
Leaving your house or apartment in Mcallen means you will likely need to take your name off of the water bill with Mcallen Public Utility. In order to take your name off the water bill, please click the link to the stop service form below. Stop service for water bills requests typically take two business days.

The estimated price of bottled water
$2.26 in USD (1.5-liter)
USER SUBMITTED RATINGS
- Drinking Water Pollution and Inaccessibility
- Water Pollution
- Drinking Water Quality and Accessibility
- Water Quality
The above data is comprised of subjective, user submitted opinions about the water quality and pollution in Mcallen, measured on a scale from 0% (lowest) to 100% (highest).
Related FAQS
Mcallen Water Quality Report (Consumer Confidence Report)
The EPA mandates that towns and cities consistently monitor and test their tap water. They must report their findings in an annual Consumer Confidence Report. Below is the most recent water quality report from Mcallen's Water. If you would like to see the original version of the report, please click here.

2020 CONSUMER CONFIDENCE REPORT
ANNUAL WATER QUALITY REPORT FOR THE PERIOD OF JANUARY 1 TO DECEMBER 31, 2020.
THIS REPORT IS INTENDED TO PROVIDE YOU WITH IMPORTANT INFORMATION ABOUT YOUR DRINKING WATER AND THE EFFORTS MADE BY MCALLEN PUBLIC UTILITY TO PROVIDE SAFE DRINKING WATER.
PWS ID NUMBER: TX1080006
A MESSAGE FROM THE GENERAL MANAGER
I am pleased at the opportunity to briefly communicate our passion here at McAllen Public Utility for providing safe, affordable, high quality drinking water to all our McAllen residents and rate payers alike. We stand by our product, our people and our water and waste water infrastructure. My hope is that all may enjoy the benefits of our staff’s outstanding commitment to servicing customers, our system’s impeccable reliability that residents have grown accustomed to and our product that is vital to a vibrant, growing community. Quality of life is comprised of several amenities, none of which are as important as affordable, safe, quality water. May we never take it for granted.
Sincerely,
Marco A. Vega, P. E.
General Manager
MPU BOARD OF TRUSTEES
The McAllen Public Utility (MPU) is governed by the McAllen Public Utility Board (MPUB), which is an elected board. The Board of Trustees of the McAllen Public Utility was created February 2, 1945 to oversee all aspects of water and wastewater for the City of McAllen. The Board consists of four members elected at large by place, in a citywide election for
Charles Amos- Chairman |
Ernest Williams- |
Mayor Javier Villalobos
Albert |
Ricardo R. |
PUBLIC PARTICIPATION OPPORTUNITIES
The McAllen Public Utility Board meets publicly on the 2nd and 4th Tuesday of each month at 4 p.m. at City Hall, 1300 Houston Ave., McAllen, Texas. These meetings are also broadcast live and recorded for viewing on MCN , which is also available for viewing at www.mcallenpublicutility.com.

Mission Statement
McAllen Public Utility is dedicated to providing clean, safe drinking water. We are committed to consistently providing quality services and quality of life to all who live, work and visit the city of McAllen. We are working hard to educate the public on the issues surrounding water use and conservation.
Superior Public Water System
McAllen Public Utility has been designated by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) a Superior Public Water System in view of the high standards of water service made available to the residents of McAllen. For over 25 years we have been recognized as a Superior Public Water Supply System, which achieves and maintains recognition for those systems who exceed the minimum acceptable standards of the TCEQ.
Our Departments
Administration
Utility Engineering
Treasury Management
Customer Relations
Billing
Meter Readers
Meter Technicians
Water Laboratory
Water Treatment Systems
Waste Water Treatment Systems
Waste Water Collections
PreTreatment
In 2020, and with a population of 175,700 people, the 2 McAllen Water Treatment Plants must now meet a minimum daily production capacity of 46.39 million gallons of water. Our current system capacities are 59.7 million gallons of treated water per day and growing.
South Water Treatment Plant: 47.0 MGD
North Water Treatment Plant: 11.2 MGD
Ground Water Well: 1.5 MGD

Source of Drinking Water
The sources of drinking water (both tap and bottled water) include rivers, lakes, streams, ponds, reservoirs, springs, and wells. As water travels over the surface of the land or through the ground, it dissolves naturally occurring minerals and, in some cases, radioactive material, and can pick up substances resulting from the presence of animals or from human activity.
Contaminants that may be present in source water include:
Microbial contaminants, such as viruses and bacteria, which may come from sewage treatment plants, septic systems, agricultural livestock operations, and wildlife.
Inorganic contaminants, such as salts and metals, which can be naturally occurring or result from urban storm water runoff, industrial or domestic wastewater discharges, oil and gas production, mining, or farming. Pesticides and herbicides, which may come from a variety of sources such as agriculture, urban storm water runoff, and residential uses.
Organic chemical contaminants, including synthetic and volatile organic chemicals, which are byproducts of industrial processes and petroleum production, and can also come from gas stations, urban storm water runoff, and septic systems.
Radioactive contaminants, which can be naturally occurring or be the result of oil and gas production and mining activities.
Our Drinking Water is Regulated
This report is a summary of the quality of the water we provide to our customers. The analysis was made using the data from the most recent Texas Commission of Environmental Quality and U.S. Environmental Protection Agency required tests and is presented in the attached pages. We hope this information helps you become more knowledgeable about your drinking water supply.
All Drinking Water May Contain Contaminants
When drinking water meets federal standards, there may not be any health benefits to purchasing bottled water or
Secondary Constituents
Many constituents such as calcium, sodium, or iron, which are often found in drinking water, can cause taste, color, or odor problems. The taste and odor constituents are called secondary constituents and are regulated by the State of Texas. These constituents are not causes for health concern; therefore, secondaries are not required to be reported in this document but they may greatly affect the appearance and taste of your water.
Required Additional Health Information for Lead
If present, elevated levels of lead can cause serious health problems, especially for pregnant women and young children. Lead in drinking water is primarily from materials and components associated with service lines and home plumbing. This water supply is responsible for providing
cannot control the variety of materials used in plumbing components. When your water has been sitting for several hours, you can minimize the potential for lead exposure by flushing your tap for 30 seconds to 2 minutes before using water for drinking or cooking. If you are concerned about lead in your water, you may wish to have your water tested. Information on lead in drinking water, testing methods, and steps you can take to minimize exposure is available from the Safe Drinking Water Hotline or at http://www.epa.gov/safewater/lead.
Special Notice
You may be more vulnerable than the general population to certain microbial contaminants, such as Cryptosporidium, in drinking water. Infants, some elderly, or immunocompromised persons such as those undergoing chemotherapy for cancer; those who have undergone organ transplants; those who are undergoing treatment with steroids; and people with HIV/AIDS or other immune system disorders can be particularly at risk from infections. You should seek advice about drinking
water from your physician or health care provider. Additional guidelines on appropriate means to lessen the risk of infection by Cryptosporidium are available from the Safe Drinking Water Hotline at (800)

Where do we get our drinking water?
The source of drinking water used by McAllen Public Utility is Surface Water.This information describes the susceptibility and types of constituents that may come into contact with your drinking water source based on human activities and natural conditions. The information contained in the assessment allows us to focus source water protection strategies. Some of this source water assessment information is available on Texas Drinking Water Watch at http://dww.tceq.state.state.tx.us/DWW. For more information on source water assessments and protection efforts at our system, please contact us. MPU receives water from the Falcon and Amistad Dams, located in Starr and Val Verde Counties, respectively.
Water Treatment Process
Our water is transferred from the Rio Grande River by the Irrigation districts into our reservoirs. A reservoir is an artificial lake used to store water. Here in the City of McAllen we have three reservoirs.
Boeye Reservoir was established in 1958. This reservoir can hold up to 180 million gallons.
The North Water Plant Reservoir was established in 2004 and can hold 200 million gallons.
The new Boeye Reservoir was established in 2011 and can hold up to 300 million gallons.
Disinfection
Disinfection is the first step in the water treatment process. In this step we will combine chlorine and sodium chlorite to generate chlorine dioxide. It is then injected into our raw water line where it will kill harmful bacteria.
Secondary Disinfection
A second disinfection process occurs by utilizing chlorine and ammonia to form chloramines. This secondary disinfection process ensures that disinfection is carried out to the distribution systems.
Flocculation
Coagulant is introduced to raw water and mixed rapidly to create a floc. Water will flow through decreasingly slower mixers allowing floc to conglomerate.
Sedimentation
After the flocculation process, water flows into a sedimentation basin. This basin allows the flocculated water to settle. A detention time of at least 6 hours is required to allow the floc to settle. The settled floc called sludge is then collected with a rake system to the center of the basin. The sludge is then disposed of to the lagoons then dewatered and hauled to sanitary landfills.
Filtration
Filtration is the final step in removing suspended matter and chlorine resistant microorganisms such as Giardia and Cryptosporidium. These filters consist of anthracite coal, and two types of sand which are coarse and fine and various sizes of gravel, which are layered on top of an under drain system.
Pumping and Storage
After the treatment process, the water is sent to storage domes which can hold up to 2 million gallons each. From there, we have high service pumps that push up to 30 million gallons in the system, including the water towers. These water towers store up to 6.75 million gallons of water.
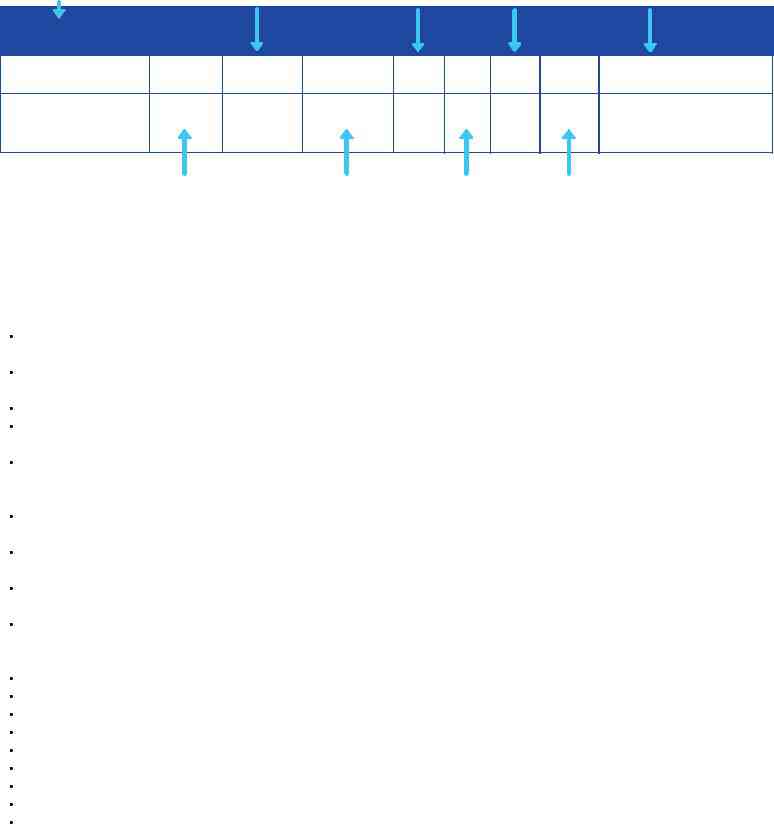
How to read your water quality report:
List of regulated, monitored, inorganic, |
The concentration of |
The lowest amount of a |
Standard |
How a contaminant |
radioactive, semivolatiles, volatile and |
the contaminant |
contaminant TCEQ or EPA |
measurement of a |
ends up in drinking |
organic compounds. |
detected. |
allows in drinking water. |
contaminant. |
water. |
CONTAMINANTS
Disinfectants and Disinfection |
Collection |
Highest Level |
Range of Levels |
MCLG |
MCL |
Units |
byproducts |
Date |
Detected |
Detected |
|
|
|
Constituent |
4/25/2016 |
4.0 |
<1.0 - 4.0 |
N/A |
50 |
ppb |
The date in which |
The amount from |
The highest amount of |
the tests were |
lowest to highest of a |
a contaminant TCEQ or |
conducted. |
contaminant detected |
EPA allows in drinking |
|
in the drinking water. |
water. |
Violation |
Likely Source of |
|
Contamination. |
||
|
||
No |
Discharge from drilling wastes; |
|
|
||
|
discharge from metal refineries; |
|
|
erosion of natural deposits. |
Whether or not there was a violation by TCEQ or EPA standards.
Definitions and Abbreviations
The following tables contain scientific terms and measures, some of which may require explanation.
Action Level: The concentration of a contaminant which, if exceeded, triggers treatment or other requirements which a water system must follow.
Action Level Goal (ALG): The level of contaminant in drinking water below which there is no known or expected risk to health. ALGs allow for a margin of safety.
Avg: Regulatory compliance with some MCLs are based on running annual average monthly samples.
Level 1 Assessment: A Level 1 assessment is a study of the water system to identify potential problems and determine (if possible) why total coliform bacteria have been found in our water system.
Level 2 Assessment: A Level 2 assessment is a very detailed study of the water system to identify potential problems and determine (if possible) why an E. coli MCL violation has occurred and/or why total coliform bacteria have been found in our water system on multiple occasions.
Maximum Contaminant Level or MCL: The highest level of a contaminant that is allowed in drinking water. MCLs are set as close to the MCLGs as feasable using the best available treatment technology.
Maximum Contaminant Level Goal or MCLG: The level of contaminant in drinking water below which there is no known or expected risk to health. MCLGs allow for a margin of safety.
Maximum Residual Disinfectant Level or MRDL: The highest level of a disinfectant allowed in drinking water. There is convincing evidence that addition of a disinfectant is necessary for control of microbial contaminants.
Maximum Residual Disinfectant Level Goal or MRDLG: The level of a drinking water disinfectant below which there is no known or expected risk to health. MRDLGs do not reflect the benefits of the use of disinfectants to control microbial contaminants.
MFL: Million Fibers per Liter (A measure of asbestos.)
MREM: Millirems per year (A measure of radiation absorbed by the body.)
na: Not aapplicable.
NTU: Nephelometric Turbidity Units (A measure of turbidity.)
pCi/L: Picocuries per liter (A measure of radioactivity.)
ppb: Micrograms per liter or parts per
ppm: Milligrams per liter or parts per
ppq: Parts per quadrillion, or picograms per liter (pg/L).
ppt: Parts per trillion, or nanograms per liter (ng/L).
|
|
|
2020 CONSUMER |
PWS ID Number: |
||||
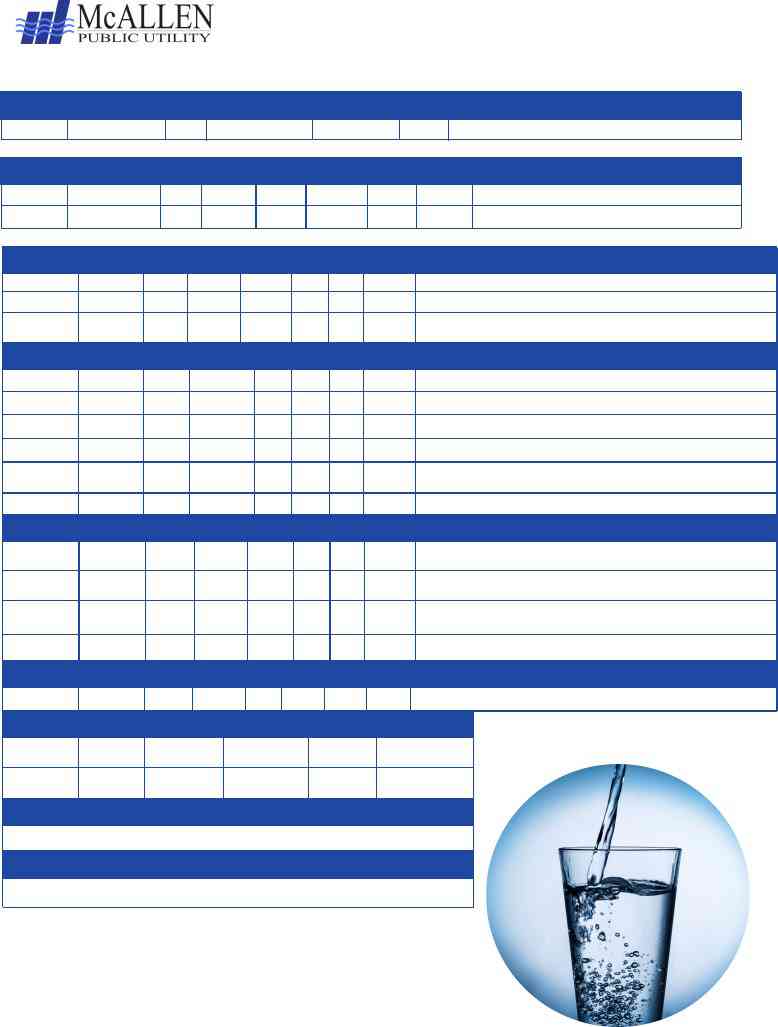
WATER QUALITY TEST RESULTS: |
CONFIDENCE REPORT |
TX1080006 |
||||||
Coliform Bacteria |
|
|
||||||
Highest |
Fecal Coliform or E. Coli |
|
|
|
|
|||
Maximum |
Total coliform |
Total no. of positive |
Violation |
Likely Source of Contamination |
||||
Contaminant |
Maximum |
No. of |
Maximum Contaminant |
Fecal Coliform or |
||||
Level Goal |
Containment Level |
Positive |
Level |
E. Coli samples |
|
|
|
|
0 |
5% of monthly samples |
0 |
0% |
0 |
No |
Present in soil, water, human, and animal digestive tract. |
||
are positive. |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Lead and copper
Lead and Date Sampled Copper
Copper |
09/01/2018 |
Lead |
09/01/2018 |
MCLG |
Action Level |
90th |
Range of |
Range of |
Violation |
Likely Source of Contamination |
|
(AL) (MCL) |
|||||||
Percentile |
Individual |
||||||
|
|
Units |
|
|
|||
1.30 |
1.30 |
0.01743 |
ppm |
No |
Corrosion of household plumbing systems; Erosion of natural |
||
deposits. |
|||||||
|
|||||||
0 |
0.015 |
0.0022 |
ppm |
No |
Corrosion of household plumbing systems; Erosion of natural |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
deposits. |
WATER QUALITY TEST RESULTS: REGULATED CONTAMINANTS |
Treatment Technique or TT: A reguired process intended to reduce the level of a contaminant in drinking water. |
Disinfection |
Collection |
Highest |
Range of |
MCLG |
|
Level |
Individual |
||||
Date |
|
||||
|
Detected |
Samples |
|
||
|
|
|
|||
Chlorite |
2020 |
0.524 |
0.8 |
||
Haloacetic Acids |
2020 |
.0135 |
.0101- No goal for |
||
(HAA5) |
.01535 |
the total |
|||
|
|
||||
Total |
2020 |
.054 |
.0238- |
No goal for |
|
Trihalomethanes |
|||||
.054 |
the total |
||||
(TTHM) |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
||
Inorganic |
Collection |
Highest |
Range of |
MCLG |
|
Level |
Individual |
||||
Contaminants |
Date |
|
|||
Detected |
Samples |
|
|||
|
|
|
|||
MCL |
Units |
Violation |
Likely Source of Contamination |
1.0 |
ppm |
No |
|
.06 |
ppm |
No |
|
.08 |
ppm |
No |
|
MCL |
Units |
Violation |
Likely Source of Contamination |
Arsenic |
2020 |
.0024 |
0.0 |
|
Barium |
2020 |
0.111 |
2.0 |
|
Cyanide |
2020 |
0.17 |
2.0 |
|
Fluoride |
2020 |
0.70 |
4.0 |
|
Nitrate |
2020 |
0.25 |
10.0 |
|
[measured as |
Nitrogen]
.01 ppm No
2.0 ppm No
2.0 ppm No
4.0 ppm No
10.0 ppm No
Erosion of natural deposits; Runoff from orchards; Runoff from glass and electronics production wastes.
Discharge of drilling wastes; Discharge from metal refineries; Erosion of natural deposits.
Discharge from plastic and fertilizer factories; Discharge from steel/metal factories.
Erosion of natural deposits; Water additive which promotes strong teeth; Discharge from fertilizer and aluminum factories.
Runoff from fertilizer use; Leaching from septic tanks, sewage; Erosion of natural deposits.
Selenium
RaddioactiveC ontaminants
2020 |
.0044 |
.05 |
.05 |
ppm |
No |
Discharge from petroleum and metal refineries; Erosion of natural deposits; Discharge from |
||
mines. |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Collection |
Highest |
Range of |
|
|
|
Violation Likely Source of Contamination |
||
Level |
Individual |
MCLG |
MCL |
Units |
||||
Date |
||||||||
Detected |
Samples |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Beta/photon |
02/13/2018 |
5.6 |
0 |
50 |
pCi/L* |
No |
Decay of natural and |
||
emitters |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Combined |
02/13/2018 |
<1.0 |
0 |
5.0 |
pCi/L |
No |
Erosion of natural deposits. |
||
Radium 226/228 |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Gross alpha |
02/13/2018 |
1.0 |
0 |
15.0 |
pCi/L |
No |
Erosion of natural deposits. |
||
excluding radon |
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
and uranium
Uranium
Disinfectant
Residual
Chloramines
Turbidity
Highest Single Measurement
Lowest monthly % meeting limit
02/13/2018 |
2.7 |
0 |
30.0 |
ug/l |
No |
Erosion of natural deposits. |
|||
Year |
Average |
Range of |
|
MRDL |
MRDLG |
Unit of |
Violation |
Source in Drinking Water |
|
Levels |
|
||||||||
|
Level |
Detected |
|
|
Measure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
2020 |
3.06 |
4.00 |
4.00 |
ppm |
No |
Water additive used to control microbes. |
|||
Year |
Level Detected |
Limit (Treatment |
Violation |
Likely Source of |
Information Statement: Turbidity is a measurement of the cloudiness of the |
||||
|
Technique) |
|
Contamination |
water caused by suspended particles. We monitor it because it is a good |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
indicator of water quality and the effectiveness of our filtration. |
2020 |
0.07 NTU |
|
0.3 NTU |
|
No |
Soil Runoff. |
|
||
2020 |
100% |
|
|
0.3 NTU |
|
No |
Soil Runoff. |
|
|
Total Organic Carbon
The percentage of Total Organic Carbon (TOC) removal was measured each month and the system met all the TOC removal requirements set, unless a TOC violation is noted in the violations section.
Water Loss
In the water loss audit submitted to the Texas Water Development Board for the time period of
*EPA considers 50 pCi/L to be the level of concern for beta particles.
*Radioactive Contaminants are sampled every 3 years as per TCEQ regulations, next due year 2021

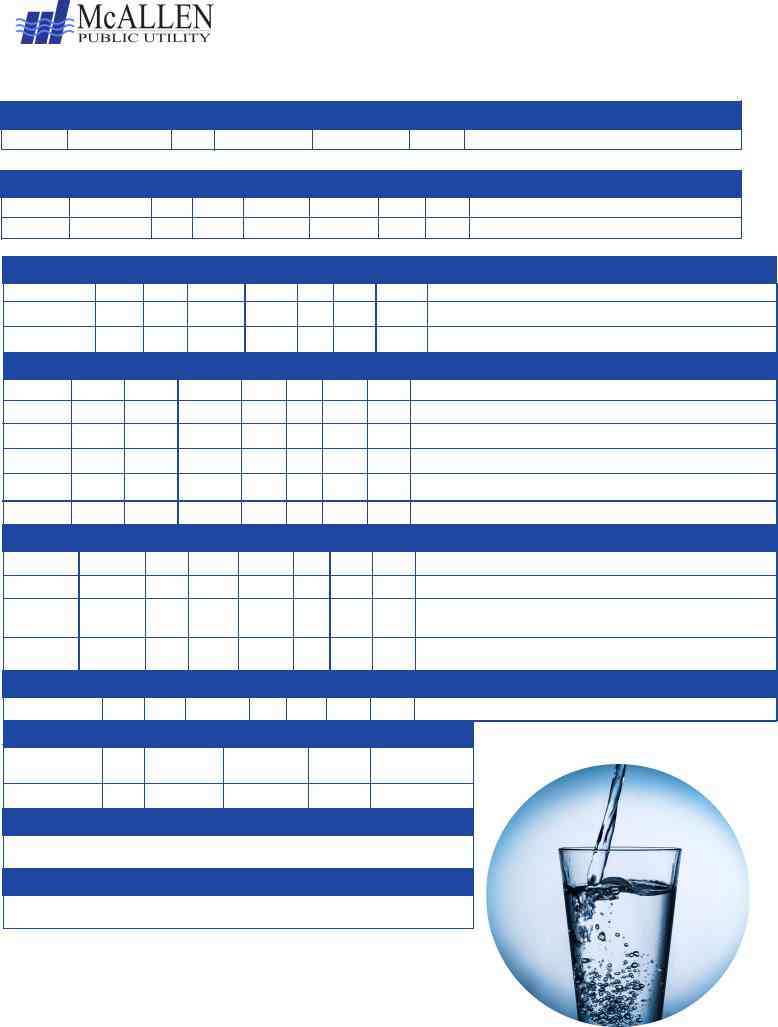
CÓMO LEER SU INFORME DE CALIDAD DEL AGUA
Lista de compuestos regulados, monitoreados, inorgánicos, radioactivos, semivolátiles, volátiles y orgánicos.
|
La cantidad más baja de un |
La concentración del |
contaminante TCEQ o EPA |
contaminante |
lo permite en el agua |
detectado |
potable. |
Medición estándar de un contaminante.
Cómo termina un contaminante en el agua potable.
CONTAMINANTES
Desinfectantes y subproductos |
Fecha de |
Nivel más alto |
Rango de niveles |
MCLG |
MCL |
Unidades |
de desinfección |
colección |
detectado |
detectados |
|
|
|
Constitucion |
4/25/2016 |
4.0 |
<1.0 - 4.0 |
N/A |
50 |
ppb |
La fecha en que se |
La cantidad de un |
La cantidad más alta de |
realizaron las |
contaminante |
un contaminante TCEQ |
pruebas. |
detectado en el agua |
o EPA lo permite en el |
|
potable de menor a |
agua potable. |
|
mayor. |
|
Violación Probable fuente de contaminación.
No |
Descarga de desechos de |
|
perforación; descarga de refinerías |
||
|
||
|
de metales; erosión de depósitos |
|
|
naturales |
Si existe o no una violación según las normas de TCEQ o EPA.
Definiciones y Abreviaturas
Las siguientes tablas contienen términos y medidas científicas, algunas de las cuales pueden requerir una explicación.
AL: Nivel de acción. Grado de concentración de un contaminante que, al ser excedido, se debe llevar a cabo un tratamiento u otros requisitos a los cuales se debe tener un sistema de abastecimiento de agua.
Objetivo del nivel de acción (ALG): El nivel de un contaminante en el agua potable por debajo del cual no existe un riesgo conocido o esperado para la salud. Las ALG permiten un margen de seguridad.
Promedio (Avg): El cumplimiento normativo con algunos MCL se basa en el promedio anual de muestras mensuales.
Evaluación de grado 1: Una evaluación de grado 1 es un estudio del acueducto para identificar posibles problemas, y de ser factible, determinar la causa de la presencia de coliformes totales.
Evaluación de grado 2: Una evaluación de grado 2 es un estudio detallado del acueducto para identificar posibles problemas, y de ser factible, determinar por qué se exedió el grado de contaminación máximo (MCL por sus siglas en inglés) de Escherichia coli (E. coli) y/o porqué se detectaron coliformes totales en múltiples ocasiones.
MCL: Grado máximo de contaminantes es el grado más alto de un contaminante que se permite en el agua potable. Los MCL se establecen lo más cerca posible a los MCLG mediante el uso de la tecnología disponible más avanzada de saneamiento. MCLG: Meta máxima en el nivel de contaminantes es el grado de concentración de un contaminante en el agua potable por debajo del cuál no existe o no se espera que haya un riesgo conocido para la salud. Los MCLG ofrecen un margen de seguridad. MRDL (por sus siglas en inglés): Nivel máximo residual de desinfectante es el nivel más alto de desinfectante permitido en el agua potable. Hay evidencia convincente que es necesaria la adición de un desinfectante para controlar los contaminantes microbianos.
MRDLG (por sus siglas en inglés): Objetivo de nivel máximo residual de desinfectante es el nivel de desinfectante en el agua potable bajo el cuál no se conocen o se espera causar riesgo a la salud. Los MRDLG no reflejan los beneficios del uso de desinfectantes para controlar los contaminantes microbianos.
MFL: millones de fibras por litro (una medida de amianto)
mrem/año: Milirems por año (unidades de radiación absorbidas por el cuerpo).
na: no aplica
NTU: Unidades nefelométricas de turbidez. Unidades que miden la turbidez del agua.
pCi/L: Picocuries por litro (una medida de la radiactividad).
ppb: Partes por mil millones o microgramos por litro.
ppm: Partes por millon, o miligramos por litro
ppq: Partes por quadrillon, o picogramas
ppt: Partes por trillon o nanogramos por litro
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2020 INFORME SOBRE LA |
PWS ID Number: |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CALIDAD DEL AGUA POTABLE |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
TX1080006 |
||||||||
RESULTADOS DE LA PRUEBA DE CALIDAD DEL AGUA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Bacterias Coliformes |
|
|
|
El más alto |
Nivel máximo de |
Total no. de coliformes |
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Meta del Nivel |
|
|
Nivel máximo de |
|
|
Violación |
Procedencia del contaminante |
|||||||||||
Máximo de |
|
|
contención de |
|
|
número de |
coliformes fecales o |
|
fecales positivos o |
|||||||||
Contaminante |
|
coliformes totales |
positivos |
|
E. coli |
|
Muestras de E. Coli |
|
|
|
|
|||||||
0 |
5% de las muestras |
|
|
0 |
|
0% |
|
0 |
|
|
No |
Presente en el tracto digestivo del suelo, agua, humanos y animales |
||||||
|
mensuales son positivas. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Plomo y Cobre |
|
|
|
|
|
Action Level |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
90 ° |
|
Rango de |
Unidades |
|
Violación |
Procedencia del contaminante |
|||
Plomo y Cobre |
|
Fecha de muestra |
|
MCLG |
(AL) (MCL) |
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
percentil |
|
Individual |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cobre |
|
|
09/01/2018 |
|
|
1.30 |
1.30 |
0.01743 |
ppm |
|
No |
Corrosión de la tubería doméstica, erosión de depósitos naturales. |
||||||
Plomo |
|
|
09/01/2018 |
|
|
0 |
0.015 |
0.0022 |
ppm |
|
No |
Corrosión de la tubería doméstica, erosión de depósitos naturales. |
||||||
CONTAMINANTES |
Técnica de tratamiento o TT: un proceso requerido para reducir el nivel de un contaminante en el agua potable. |
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
Nivel más |
Rango de |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Productos |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
REGULADOS |
|
|
Fecha de |
|
|
alto |
muestras |
MCLG |
MCL |
Unidades |
Violación |
Procedencia del contaminante |
|
|||||
derivados de la |
|
muestra |
detectado |
|
||||||||||||||
desinfección |
|
|
individuales |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Clorito |
|
|
|
2020 |
|
|
|
0.524 |
0.8 |
1.0 |
ppm |
No |
|
Subproducto de la desinfección del agua potable. |
||||
Ácidos |
|
|
|
2020 |
|
|
|
.0135 |
Sin objetivo |
.06 |
ppm |
No |
|
Subproducto de la desinfección del agua potable. |
||||
Haloacéticos (HAA5) |
|
|
|
para el total |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Trihalometanos |
|
|
2020 |
|
|
|
.054 |
Sin objetivo |
.08 |
ppm |
No |
|
Subproducto de la desinfección del agua potable. |
|||||
totales (TTHM) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
para el total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contaminantes |
Fecha de |
Nivel más |
Rango de |
MCLG |
MCL |
|
alto |
muestras |
|||||
Inorgánicos |
muestra |
|||||
detectado |
individuales |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
Arsenico |
2020 |
.0024 |
0.0 |
.01 |
||
Bario |
2020 |
0.111 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
||
Cianuro |
2020 |
0.17 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
||
Fluoruro |
2020 |
0.70 |
4.0 |
4.0 |
||
|
||||||
Nitrato |
2020 |
0.25 |
10.0 |
10.0 |
||
(como N) |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
Selenio |
2020 |
.0044 |
.05 |
.05 |
Unidades |
Violación |
Procedencia del contaminante |
|
ppm |
No |
Erosión de depósitos naturales; Aguas contaminadas por desechos provenientes de huertas |
|
|
y la de producción de vidrio y la electrónica. |
||
|
|
||
ppm |
No |
Efluentes de desechos de perforación o de refinerías de metales, erosión de depósitos |
|
naturales. |
|||
|
|
||
ppm |
No |
Efluentes de las fábricas de acero y metales; efluentes de fábricas de plásticos y |
|
fertilizantes |
|||
|
|
||
ppm |
No |
Erosión de depósitos naturales; aditivo para fomentar la salud dental; efluentes de fabricas |
|
de fertilizantes y de aluminnio |
|||
|
|
||
ppm |
No |
Aguas contaminadas por el uso de fertilizantes; lixiviación de tanques sépticos y redes de |
|
alcantarillados, erosión de depósitos naturales |
|||
|
|
||
ppm |
No |
Descarga de refinerías de petróleo y metal; Erosión de depósitos naturales; Descarga de |
|
minas. |
|||
|
|
|
Fecha de |
Nivel más |
Rango de |
MCLG |
|
Radioactivo |
alto |
muestras |
|||
muestra |
|||||
|
|||||
|
|
detectado |
individuales |
|
|
Emisores de |
02/13/2018 |
5.6 |
0 |
||
Beta / fotones |
|||||
|
|
|
|
||
Radio combinado |
02/13/2018 |
<1.0 |
0 |
||
226/228 |
|
|
|
|
|
Alfa excluyendo |
02/13/2018 |
1.0 |
0 |
||
el radón y el |
|||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
||
uranio |
|
|
|
|
|
Uranio |
02/13/2018 |
2.7 |
0 |
MCL |
Unidades |
Violación |
Procedencia del contaminante |
50.0 |
pCi/L* |
No |
Desintegración radiactiva de depósitos naturales y artificiales. |
5.0 |
PCi/L |
No |
Erosión de depósitos naturales |
15.0 |
pCi/L |
No |
Erosión de depósitos naturales |
|
|
||
30.0 |
ug/l |
No |
Erosión de depósitos naturales |
Disinfectant |
Año |
Nivel |
Rango de |
MRDL |
MRDLG Unidades Violación Fuente en el agua potable |
|
promedio |
niveles |
|||||
Residual |
||||||
|
|
detectados |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Cloraminas |
2020 |
|
Turbidez |
Año |
|
|
||
Medida única más alta |
2020 |
|
El menor % mensual |
2020 |
|
cumple con el límite |
||
|
Carbono Orgánico Total
3.06 |
4.00 |
4.00 |
ppm |
|
Nivel detectado |
Límite (técnica de |
Violación |
||
|
|
tratamiento) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0.07 NTU |
|
0.3 NTU |
|
No |
|
|
|
||
100% |
|
0.3 NTU |
|
No |
No Aditivo de agua utilizado para controlar los microbios.
Probable fuente |
Declaración de información: la turbidez es una medida de la nubosidad del |
|
de contaminación |
||
agua causada por partículas en suspensión. Lo monitoreamos porque es un |
||
|
||
La escorrentía |
buen indicador de la calidad del agua y la efectividad de nuestra filtración. |
|
|
||
del suelo. |
|
|
La escorrentía |
|
|
del suelo. |
|
El porcentaje de eliminación de carbono orgánico total (TOC) se midió cada mes y el sistema cumplió con todos los requisitos de eliminación de TOC establecidos, a menos que se observe una violación de TOC en la sección de violaciones.
Perdida de agua
En la auditoría de pérdida de agua presentada a la Junta de Desarrollo del Agua de Texas para el período de enero a diciembre de 2020, nuestro sistema perdió un estimado de 10.69% de agua. Si tiene alguna pregunta sobre la auditoría de pérdida de agua, llame al

HAVE QUESTIONS REGARDING
YOUR WATER AT
YOUR HOME, SCHOOL, OR
BUSINESS? Directory
Customer Service: |
|
Utility Administration: |
|
Water Plant: |
|
Waste Water Plant: |
|
Pretreatment: |
|
After Hours: |
Address
1300 W Houston Ave
McAllen, TX 78501
hours
Lobby: Monday- Friday
8:00AM to 5:00PM
7:30AM to 5:30PM
find us online
McAllenPublicUtility.com

A look back at 2020

Contaminants
McAllen Public Utility
EWG's drinking water quality report shows results of tests conducted by the water utility and provided to the Environmental Working Group by the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality, as well as information from the U.S. EPA Enforcement and Compliance History database (ECHO). For the latest quarter assessed by the U.S. EPA (January 2019 - March 2019), tap water provided by this water utility was in compliance with federal health-based drinking water standards.
Utility details
- Serves: 168909
- Data available: 2012-2017
- Data Source: Surface water
- Total: 30
Contaminants That Exceed Guidelines
- Arsenic
- Bromodichloromethane
- Bromoform
- Chlorate
- Chlorite
- Chloroform
- Dibromochloromethane
- Dichloroacetic acid
- Radium%2C combined (-226 & -228)
- Total trihalomethanes (TTHMs)
- Uranium
Other Detected Contaminants
- 1%2C4-Dioxane
- Aluminum
- Barium
- Bromochloroacetic acid
- Bromochloromethane
- Chromium (hexavalent)
- Chromium (total)
- Cyanide
- Dibromoacetic acid
- Fluoride
- Haloacetic acids (HAA5)
- Manganese
- Molybdenum
- Monobromoacetic acid
- Nitrate
- Selenium
- Strontium
- Trichloroacetic acid
- Vanadium
Reminder
Always take extra precautions, the water may be safe to drink when it leaves the sewage treatment plant but it may pick up pollutants during its way to your tap. We advise that you ask locals or hotel staff about the water quality. Also, note that different cities have different water mineral contents.
Sources and Resources
Sources Cited
Additional Resources
Mcallen Tap Water
McAllen Texas, tap water is nothing to be proud of. It is downright scary. Have you ever wondered what exactly goes into the water that is pumped up your sink? How much harm could be done with this?
The answer to that question is not good. For starters, we are putting more chemicals in our drinking water than we ever have before. These chemicals are getting into our skin and our bodies in massive amounts. This is a real problem because many of these chemicals, once absorbed, slowly attach to our bodies and cause various illnesses. Some of the most common are cancer, organ toxicity, nerve damage, and hormonal problems.
Suppose you are serviced by the McAllen Tx powerplant responsible for the massive pollution in Texas. In that case, you are living in a heavily polluted environment. The Environmental Protection Agency and the Safe Drinking Water Act were not designed to address the level of pollution in our reservoir system. They were put in place to protect the natural water supply of our country. Still, we have already done that work for them. We need to be careful how and where we treat our water and make sure that it is pure and healthy.
Mcallen Drinking Water
McAllen, TX is a large city located in rural SE, Texas. The city is considered central Texas in the United States; however, it is one of Texas’s most populated cities. It is an excellent place for anyone who enjoys living in an urban environment. While the city is booming and has many potentials, some say that the city’s growth is stifling the natural water flow from underground aquifers. There have been many cases where the chemicals that makeup chlorine have caused the water to turn acidic, making the people in the drinking water source very sick.
Many people are worried about the chemicals that may be in the drinking water of McAllen, TX. The Texas Railroad Commission is responsible for ensuring that the water coming into the city is clean enough for drinking purposes. However, this commission was recently asked to investigate whether or not the chemicals were causing damage to the natural water supplies of the city. Because the number of chemicals that make up the chlorine in a typical bottle of McAllen water can be hazardous, this commission was also asked to look into the possible causes of this problem.
The EPA is also responsible for ensuring that the drinking water of every American is safe from harm. When you go to your local grocery store or do a search on the Internet, you will likely find that most of the sold brands contain some level of chlorine. While it is essential to buy bottled water to avoid drinking water that has been affected by chemicals, it is also necessary to find a brand of water that does not contain any bleach or similar chemical that can potentially harm you when you consume it. When searching for a good brand of McAllen water, your best bet is to purchase one produced in the hometown of Mcallen, TX. This means that the water will have been filtered at home before being sent to homes across Texas.
Water Quality in Mcallen
If you own a home in Mcallen, TX, you know you have one of the best water quality in the world. This is because the amount of pollutants, such as arsenic, in the groundwater and the soil of this area is meager. This allows for various natural wildlife, including migratory birds and different species of plants, to take shelter here. Deer, geese, and several kinds of waterfowl call this area their home. Because of all this, it is a good idea to have your water quality tested by a company specializing in this type of testing.
It is essential to know that not every company that offers to test for water quality in Mcallen, TX, can also test other important things. For example, some will test for bacteria and viruses, while others will only test for salt and acidity levels. When it comes to having your water quality tested, the two main concerns are the safety and quality of the end product. Suppose a company is only testing for safety. In that case, you don’t want to invest in that company because they aren’t going to provide you with the best quality water or service. Instead of spending your money on one of those companies that provides quality testing, you should spend your money on one that provides both.
Before you spend any of your money testings for water quality in Mcallen, TX, it is a good idea to check out the quality of the testing lab that is doing the testing. Some of the better labs will test for certain metals like lead, which can be extremely harmful if consumed in any manner. Other contaminants may not show up in the test, so that you might get a false positive. Still, a reliable company should be able to confirm that there are no issues with the water. It also helps to check out the reputation of the company as well. Many people have had problems with water that they have delivered to their homes. Hence, it pays to find a company that is known for providing great water.
Mcallen Water Treatment
McAllen Texas water treatment and filtration systems have long been known for quality. They are recognized as the leader in water treatment and filtration in the world. They provide a clean water supply for all of those living in the McAllen area. They provide chlorination of water, which is the process used to kill any harmful bacteria or other pollutants that might find their way into your local water supply. This process is considered to be the most effective method of water purification available today. Since it is so effective, it is often referred to as the “state miracle.”
It would be best if you took special note of how your water is treated at your local treatment facility. You need to learn about what they use to treat your water so that you can choose the right McAllen Texas water treatment system for your family. In addition to learning about their process, you may also want to know about their equipment. It’s best to go with a system that uses a countertop or point-of-use units. These are the most effective in terms of ease of use and the least expensive to buy.
Your home is probably the important place in your life. Make sure that your home is protected from threats. Choose the right McAllen, Texas water filtration system today to make your home safe for your family. You’ll be glad you did when you see how wonderful your home looks after you have gone through the process. The peace of mind alone is worth the investment.
Mcallen Water Supply
There are many reasons why a person would need to have the Mcallen TX water supply. This type of filtration system will be able to remove any contaminants or other materials from your water. It is also going to be very efficient at doing this. Here are some things about this type of filtration system that you should take a look at.
The first thing that people will need to realize is that this is one filtration system capable of cleaning chemicals and other materials from your water. In most cases, it can get rid of viruses, bacteria, parasites, and much more. Another essential thing to see is that this system can easily remove sediment and rust as well. It is even capable of cleaning out heavy metals from your water supply.
Something else to see about the Mcallen TX water supply filter is that it can provide you with clean, pure water. When you compare this with your regular drinking water supply, you will see that there can be a huge difference. This means that you will not have to worry about drinking contaminated water. This is especially critical for people who may have specific health problems. It will help to make sure that they have the cleanest water possible.
Mcallen Water System
“I have found McAllen, TX to be a great place to purchase a home water system. The people in this area are very friendly and you don’t have to worry about running out of running water or waiting on a long line to get any service. I’ve purchased several systems from them and they have worked great for me. I highly recommend them to anyone looking for a quality water system.” – Karen B., Fort Worth.
“My family has had the pleasure of using McAllen, TX water supply for over thirty years. During that time, we have never ran out of service and always been satisfied with the quality of our water. I recommend this company to everyone who is building a house or adding a new home.” – Steve W., Fort Worth.
When a customer comes to McAllen, TX water system to install a home water system, they are provided with detailed instructions on making sure their new water line is connected correctly and installed securely so that there are no leaks. The professional crew that comes to your home will evaluate the type of system you have and discuss the options available to you to create the right system for your home. It is essential to discuss the options available and the type of water you have in your area to ensure that your new system is set up correctly. This ensures that your water will be reliable for years to come and that you can enjoy the satisfaction of having your own safe, clean water. You can find out more about the quality of water available through McAllen, TX, by visiting their website at McAllen Utilities.
Mcallen Water Utility
McAllen, TX, water utility companies can offer you many great deals regarding your water and sewer services. They are well known throughout the state of Texas for their reliability, and they have many different options that will benefit you when it comes to getting your water and sewer lines cleaned. You will want to look at many things when it comes to this, including the rates that they have to offer. There is also a lot of competition within the service company market, so you will need to look around to find the best prices on this.
If you need more than just your water delivered to your home, there are also many different truck mount sink systems that you can use. They will give you more storage space in your home while keeping the plumbing moving. Many people find that this is a much easier way to deal with plumbing issues that popped up in their homes over the years. Many things in our lives are more accessible when we have items in our homes that are easy to reach and advantage of. This is something that McAllen TX water utility companies are known for, and one of the many reasons they are one of the best that you can get. You don’t have to worry about any of your pipes or fixtures breaking down when you call them for help, and they can come out anytime you need them to.
When it comes to water and sewer lines, you will always need to have the right professionals take care of these repairs. The professionals available through the McAllen TX water utility companies will be top-notch no matter what you need to be done. There are many different things that you can choose from when it comes to this type of work, and knowing what you have to choose from is half the fun of having a plumbing company take care of your dirty work. Suppose you ever get in a predicament where you need some fast work done, McAllen, TX. In that case, water utility companies are the best to turn to.
Mcallen Water Contaminants
Before buying a McAllen, TX house, it is vital to have a detailed inspection of your water source. The contaminants can come from the ground, as well as the air. A quality engineer will be sent out to your property, and within a matter of days, should have all of the required testing done. These engineers will be able to determine what is in the water and where it is coming from. They can also tell you how much contamination is present. If they find anything, then you should know right away.
When the water comes back to your house, you will notice some color differences. The amount of contaminants causes this, and how fast they are converting into other forms. If you want to make sure that your water is clean, you should purchase a McAllen TX water filter. These filters will help keep your water clean and tasting great.
If you have been finding that your water is not as pure as you would like, then maybe it is time to call a McAllen TX water company for a complete analysis of your water source. By doing so, you will be able to protect your family from any possible harmful effects, and you will be able to enjoy the great water that is sent to your house. McAllen TX offers different types of filtration systems, such as Brita and PUR, both of which can provide you with water that you are satisfied with. Take a look around the internet and search for a water filtration system and one that fits your budget.
Mcallen Water Company
You’ve probably heard of McAllen, Texas water company because it’s the home of the annual Red River Festival, but did you know that they’re one of the best-known suppliers of safe, clean drinking water in Texas? The truth is, if you can find a Mcallen TX water dispenser in your community, you are giving yourself and your family the advantage of the cleaner, fresher water. This is possible is simple: all that company does is its part of making sure that your water is healthy.
When it comes to getting water from any source, several pollutants could potentially make their way into your supply. For instance, if you happen to live in a rural area that a public treatment facility doesn’t service, the chances are that you’ll be getting some level of contaminants from whatever water comes out of your tap. Moreover, since rural areas have fewer water filtering systems than urban ones, the pollutants from your supply might be spread throughout your neighborhood. If you want clean, filtered water, you need to get your water from a company that provides McAllen TX water dispensers. This way, not only will you be getting clean water from your mainline, but you’ll also be doing your part to keep contaminants out of your drinking water.
When it comes to filtering your water at home, the first thing that you need to do is purchase a quality water filter. Then, connect your water dispenser to the filter so that the filtered water can run through the entire dispenser. Finally, replace the filter on the dispenser once or twice a month. The filter in your McAllen TX water company dispenser will do an excellent job of cleaning your water and keeping harmful chemicals and pollutants out of your drinking water. So instead of drinking water that’s full of contaminants and impurities, you should always have clean, filtered water coming from your supply.