Table of Contents
Can You Drink Tap Water in Thornton?
Yes, Thornton's tap water is generally considered safe to drink as Thornton has no active health based violations of the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) that we are aware of. Other factors such as lead piping in a home, or low levels of pollutants on immunocompromised individuals, should also be considered, however. To find more recent info we might have, you can check out our boil water notice page, the city's water provider website, or Thornton's local Twitter account.
According the EPA’s ECHO database, from April 30, 2019 to June 30, 2022, Thornton's water utility, City of Thornton, had 1 non-health-based violations of the Safe Drinking Water Act. For more details on the violations, please see our violation history section below. The last violation for Thornton was resolved on May 31, 2021. This assessment is based on the City of Thornton water system, other water systems in the city may have different results.
While tap water that meets the EPA health guidelines generally won’t make you sick to your stomach, it can still contain regulated and unregulated contaminants present in trace amounts that could potentially cause health issues over the long-run. These trace contaminants may also impact immunocompromised and vulnerable individuals.
The EPA is reviewing if it’s current regulations around pollutant levels in tap water are strict enough, and the health dangers posed by unregulated pollutants, like PFAS.
Water Quality Report for Thornton Tap Water
The most recent publicly available numbers for measured contaminant levels in Thornton tap water are in its 2020 Water Quality Report. As you can see, there are levels which the EPA considers to be acceptable, but being below the maximum allowable level doesn’t necessarily mean the water is healthy.
Lead in tap water, for example, is currently allowed at up to 15ppb by the EPA, but it has set the ideal goal for lead at zero. This highlights how meeting EPA standards doesn’t necessarily mean local tap water is healthy.
EPA regulations continue to change as it evaluates the long term impacts of chemicals and updates drinking water acceptable levels. The rules around arsenic, as well as, lead and copper are currently being re-evaluated.
There are also a number of "emerging" contaminants that are not currently. For example, PFAS (Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances), for which the EPA has issued a health advisory. PFAS are called "forever chemicals" since they tend not to break down in the environment or the human body and can accumulate over time.
We recommend looking at the contaminants present in Thornton's water quality reports, or getting your home's tap water tested to see if you should be filtering your water.
Thornton Tap Water Safe Drinking Water Act Violation History - Prior 10 Years
Below is a ten year history of violations for the water system named City of Thornton for Thornton in Colorado. For more details please see the "What do these Violations Mean?" section below.
From May 1, 2021 to May 31, 2021, Thornton had 1 non-health based Safe Drinking Water Act violation with the violation category being Monitoring and Reporting, more specifically, the violation code was Monitoring, Turbidity (Enhanced SWTR) which falls into the Microbials rule code group, and the Surface Water Treatment Rules rule code family for the following contaminant code: Interim Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule.
Is there Lead in Thornton Water?
Based on the EPA’s ECHO Database, 90% of the samples taken from the Thornton water system, City of Thornton, between sample start date and sample end date, were at or below, 0.0022 mg/L of lead in Thornton water. This is 14.7% of the 0.015 mg/L action level. This means 10% of the samples taken from Thornton contained more lead.
While Thornton water testing may have found 0.0022 mg/L of lead in its water, that does not mean your water source has the same amount. The amount of lead in water in a city can vary greatly from neighborhood to neighborhood, or even building to building. Many buildings, particularly older ones, have lead pipes or service lines which can be a source of contamination. To find out if your home has lead, we recommend getting you water tested.
No amount of lead in water is healthy, only less dangerous. As lead accumulates in our bodies over time, even exposure to relatively small amounts can have negative health effects. For more information, please check out our Lead FAQ page.
Are there PFAS in Thornton Tap Water?
Currently, testing tap water for PFAS isn’t mandated on a national level. We do have a list of military bases where there have been suspected or confirmed leaks. There appears to be at least one military base - Lowry Air Force Base - near Thornton with suspected leaks.
With many potential sources of PFAS in tap water across the US, the best information we currently have about which cities have PFAS in their water is this ewg map, which you can check to see if Thornton has been evaluated for yet.
Our stance is better safe than sorry, and that it makes sense to try to purify the tap water just in case.
Thornton SDWA Violation History Table - Prior 10 Years
| Compliance Period | Status | Health-Based? | Category Code | Code | Rule Code | Contaminant Code | Rule Group Code | Rule Family Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05/01/2021 - 05/31/2021 | Resolved | No | Monitoring and Reporting (MR) | Monitoring, Turbidity (Enhanced SWTR) (38) | Long Term 1 Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule (122) | Interim Enhanced Surface Water Treatment Rule (0300) | Microbials (100) | Surface Water Treatment Rules (120) |
What do these Violations Mean?
Safe Drinking Water Act Violations categories split into two groups, health based, and non-health based. Generally, health based violations are more serious, though non-health based violations can also be cause for concern.
Health Based Violations
- Maximum contaminant levels (MCLs) - maximum allowed contaminant level was exceeded.
- Maximum residual disinfectant levels (MRDLs) - maximum allowed disinfectant level was exceeded.
- Other violations (Other) - the exact required process to reduce the amounts of contaminants in drinking water was not followed.
Non-Health Based Violations
- Monitoring and reporting violations (MR, MON) - failure to conduct the required regular monitoring of drinking water quality, and/or to submit monitoring results on time.
- Public notice violations (Other) - failure to immediately alert consumers if there is a serious problem with their drinking water that may pose a risk to public health.
- Other violations (Other) - miscellaneous violations, such as failure to issue annual consumer confidence reports or maintain required records.
SDWA Table Key
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Compliance Period | Dates of the compliance period. |
| Status |
Current status of the violation.
|
| Health-Based? | Whether the violation is health based. |
| Category Code |
The category of violation that is reported.
|
| Code | A full description of violation codes can be accessed in the SDWA_REF_CODE_VALUES (CSV) table. |
| Contaminant Code | A code value that represents a contaminant for which a public water system has incurred a violation of a primary drinking water regulation. |
| Rule Code |
Code for a National Drinking Water rule.
|
| Rule Group Code |
Code that uniquely identifies a rule group.
|
| Rule Family Code |
Code for rule family.
|
For more clarification please visit the EPA's data dictionary.
Thornton Water - Frequently Asked Questions
| By Phone: | 303-255-7776 |
| By Email: | hsueh.shih@thorntonco.gov |
| By Mail: | 9500 CIVIC CENTER DR THORNTON, CO, 80229 |
Existing customers can login to their City of Thornton account to pay their Thornton water bill by clicking here.
If you want to pay your City of Thornton bill online and haven't made an account yet, you can create an account online. Please click here to create your account to pay your Thornton water bill.
If you don't want to make an account, or can't remember your account, you can make a one-time payment towards your Thornton water bill without creating an account using a one time payment portal with your account number and credit or debit card. Click here to make a one time payment.
Moving to a new house or apartment in Thornton means you will often need to put the water in your name with City of Thornton. In order to put the water in your name, please click the link to the start service form below. Start service requests for water bills typically take two business days.
Leaving your house or apartment in Thornton means you will likely need to take your name off of the water bill with City of Thornton. In order to take your name off the water bill, please click the link to the stop service form below. Stop service for water bills requests typically take two business days.

The estimated price of bottled water
$1.25 in USD (1.5-liter)
USER SUBMITTED RATINGS
- Drinking Water Pollution and Inaccessibility
- Water Pollution
- Drinking Water Quality and Accessibility
- Water Quality
The above data is comprised of subjective, user submitted opinions about the water quality and pollution in Thornton, measured on a scale from 0% (lowest) to 100% (highest).
Related FAQS
Thornton Water Quality Report (Consumer Confidence Report)
The EPA mandates that towns and cities consistently monitor and test their tap water. They must report their findings in an annual Consumer Confidence Report. Below is the most recent water quality report from Thornton's Water. If you would like to see the original version of the report, please click here.

2021
WATER QUALITY REPORT
The city of Thornton is pleased to present the
2021 Consumer Confidence Report.
Thornton’s Water Sources
This report provides an overview of water quality samples and analyses performed in 2020. Staff members monitor the drinking water from where it starts as snowmelt in the headwaters
of the South Platte River basin, throughout the treatment process and distribution system, to where it ends at customers’ taps. The city’s Water Quality Laboratory analyzes water samples for numerous contaminants to ensure your water is safe to drink. Most importantly, microbiological tests are performed to detect for the presence of dangerous pathogens. While there was a slight slowdown due to COVID related closures
and precautions, water quality personnel still collected more than 2,500 water samples and performed more than 27,000 analytical tests in 2020. This report summarizes the testing for the year and presents other information that is important to know. In 2020, no state or federal drinking water standards were exceeded. In addition, Thornton analyzed for many other unregulated contaminants and did not detect any issues. Please contact Water Quality if you have further questions or would like to know more recent and localized water quality data.
Thornton’s drinking water starts as snowmelt in the mountains.
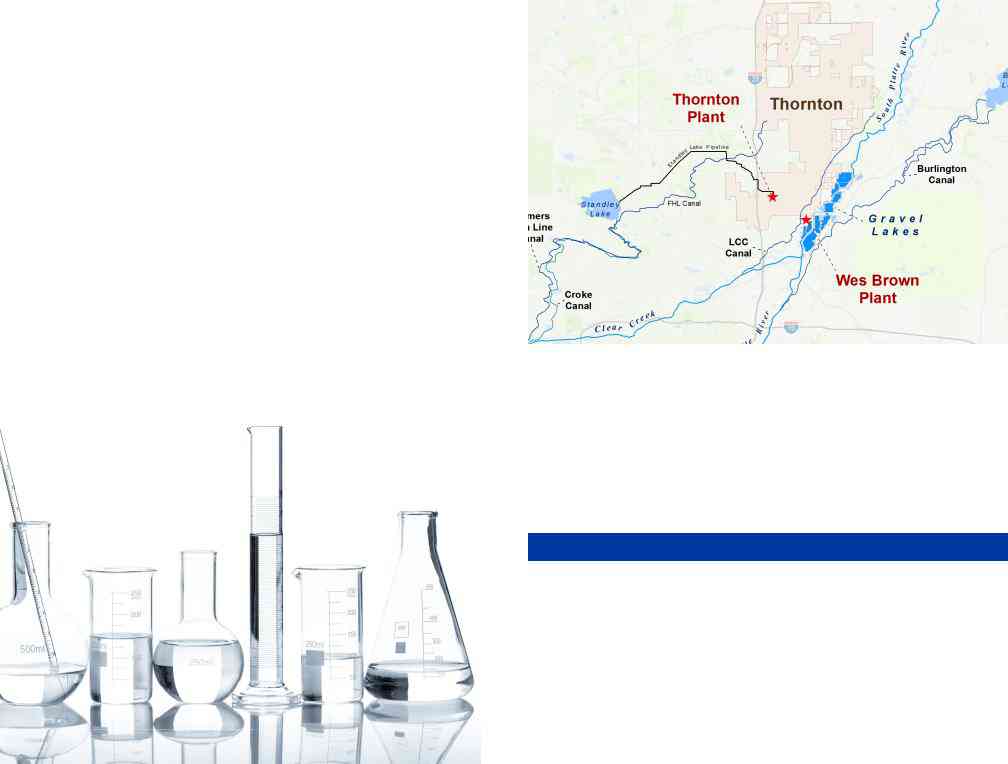
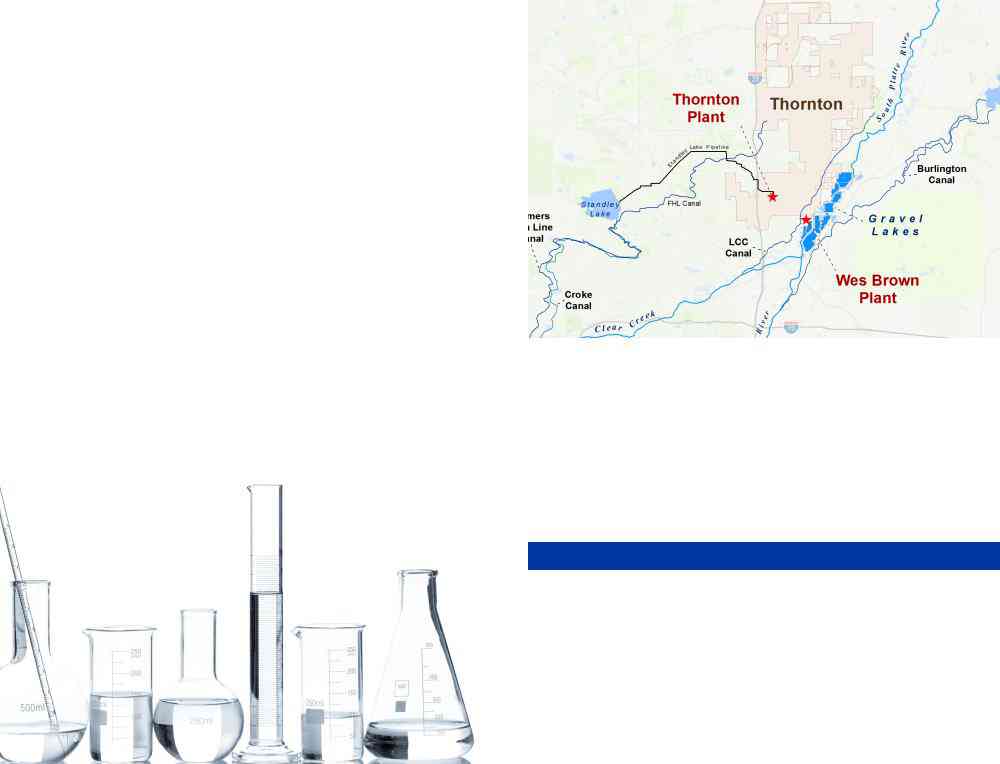
The city owns water rights in the South Platte River, Clear Creek, and Cache la Poudre River. South Platte water is diverted north of Denver and stored in a network of gravel lakes before treatment. The majority of Clear Creek water is stored in Standley Lake, while a smaller portion is diverted into the gravel lakes in Thornton. The city is currently working hard to deliver water to its customers from the Cache la Poudre River by 2025.
SWAP: Source Water Assessment and Protection Report
In 2002, the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment (CDPHE) conducted a statewide Source Water Assessment for
all municipal drinking water providers. The report identified potential sources of contaminants, such as gasoline storage tanks, wastewater plant discharges,
mine drainages and others. These sites do not necessarily pose a threat but were identified only as potential sources of contamination. Thornton uses this information to ensure all routine monitoring includes these potential contaminants.
View the report at www.ThorntonCO.gov/SWAP.

Health
All drinking water, including bottled water, may reasonably be expected to contain at least small amounts of some contaminants. The presence of contaminants does not necessarily indicate that the water poses a health risk. However, some people may be more vulnerable to contaminants in drinking water than the general population. Immunocompromised persons such as persons with cancer undergoing chemotherapy, persons who have undergone organ transplants, people with
In order to ensure that tap water is safe to drink, CDPHE prescribes regulations that limit the amount of certain contaminants in water provided by public water systems. The Food and Drug Administration regulations establish limits for contaminants in bottled water that must provide the same protection for public health.
The sources of drinking water (both tap water and bottled water) such as rivers, lakes and streams, contain naturally occurring minerals, including radioactive material, that are not completely removed at the water treatment plant and can pose a human health risk if present at a concentration above the safe levels set by the EPA. Contaminants that may be present in source water include:
-
Microbial contaminants, such as viruses and bacteria that may come from sewer treatment plants, septic systems, agricultural livestock operations, and wildlife. EPA and Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines on appropriate means to lessen the risk of infection by Cryptosporidium and other microbial contaminants are available from the Safe Drinking Water Hotline
(1-800-426-4791). It is important to note that, according to the EPA, CDC, and other health agencies, there has been no evidence that the currentCOVID-19 coronavirus can be transmitted through drinking water. -
Inorganic contaminants, such as salts and metals, which can be
naturally-occurring or result from urban stormwater runoff,
Information
industrial or domestic wastewater discharges, oil and gas production, mining, or farming.
-
Lead, if present at elevated levels, can cause serious health problems, especially for pregnant women and young children. Lead in drinking water is primarily from materials and components associated with service lines and home plumbing. Thornton is responsible for providing high quality drinking water, but cannot control the variety of materials used in plumbing components. When your water has been sitting for several hours, you can minimize the potential for lead exposure by flushing your tap for 30 seconds to two minutes before using water for drinking or cooking.
Thornton does not install lead service lines and elevated lead levels have not been detected in the city. However, you may wish to have your water tested if you are concerned about lead in your water. Information on lead in drinking water, testing methods, and steps you can take to minimize exposure is available from the Safe Drinking Water Hotline(1-800-426-4791) or at http://www.epa.gov/ safewater/lead. - Pesticides and herbicides that may come from a variety of sources, such as agriculture, urban stormwater runoff, and residential uses.
- Organic chemical contaminants, including synthetic and volatile organic chemicals, which are byproducts of industrial processes and petroleum production, and also may come from gas stations, urban stormwater runoff, and septic systems.
- Radioactive contaminants, that can be naturally occurring or be the result of oil and gas production and mining activities.
For more information about contaminants and potential health effects call the EPA Safe Drinking Water Hotline at
Thornton Water |
|
In 2020, no state or federal drinking |
||||||
|
|
|
|
water standards were exceeded. |
||||
|
PRIMARY STANDARDS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contaminant |
MCL |
MCLG |
Range of Detected Results |
Units |
Typical Sources |
Violation? |
|
|
(min - max) |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discharge from petroleum |
|
|
|
Antimony |
6 |
n/a |
0.44 |
ppb |
refineries, fire retardants, |
No |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ceramics, electronics, solder |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Erosion of natural deposits, |
|
|
|
Arsenic |
50 |
n/a |
1.2 |
ppb |
runoff from orchards, glass |
No |
|
|
and electronics |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
production wastes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discharge of oil drilling |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
wastes and |
|
|
|
Barium |
2,000 |
2,000 |
41 - 51 |
ppb |
from metal refineries, erosion |
No |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
natural deposits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discharge from steel and pulp |
|
|
|
Chromium |
100 |
100 |
1.1 - 1.5 |
ppb |
mills and chrome plating, |
No |
|
|
erosion of natural |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
deposits |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Erosion of natural deposits, |
|
|
|
Nickel |
100 |
n/a |
1.3 - 5.2 |
ppb |
discharge |
No |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
from metal factories |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discharge from petroleum, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
glass and metal refineries, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
erosion of natural deposits, |
|
|
Definitions
PRIMARY STANDARDS:
EPA has established National Primary Drinking Water Regulations (NPDWRs.) Legally enforceable standards that apply to public water systems. These standards protect drinking water quality by limiting the levels of specific contaminants that can adversely affect public health and which are known or anticipated to occur in public water supplies.
SECONDARY STANDARDS:
EPA has established National Secondary Drinking Water Regulations (NSDWRs) that set
Selenium |
50 |
50 |
1.3 - 1.7 |
ppb |
discharge from mines and |
No |
|
|
|
|
|
|
chemical manufacturers, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
runoff from livestock lots |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(feed additive) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fluoride |
4 |
4 |
0.37 - 1.22 |
ppm |
Erosion of natural deposits; |
No |
|
Thornton does not fluoridate |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nitrate |
10 |
n/a |
0.1 - 1.61 |
ppm |
Fertilizer, septic tanks, sewer |
No |
|
|
|
|
|
|
plant discharges, naturally |
|
|
Nitrite |
1 |
n/a |
0.05 |
ppm |
|
||
occurring deposits |
No |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AL > 15 |
|
0.5 - 38 |
ppb |
Household plumbing, battery |
|
|
Lead |
0 |
90% samples ≤ 2.4 - 2.5 |
manufacturing, erosion of |
No |
|||
90% samples ≤ 15 |
|||||||
|
|
2 sites >15 |
|
natural deposits |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AL > 1,300 |
|
9.8 - 1,430 |
ppb |
Household plumbing, wood |
|
|
Copper |
1,300 |
90% samples ≤ 720 - 969 |
preservatives, erosion of |
No |
|||
90% samples ≤ 1,300 |
|||||||
|
|
3 sites >1,300 |
|
natural deposits |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Disinfectants |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chlorine |
RAA ≤ 4 |
4 |
1.89 - 2.79 |
ppm |
Added in the water treatment |
No |
|
(as Chloramine) |
RAA = 2.46 |
process |
|||||
Organic Chemicals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Removal Ratio |
|
|
|
Naturally occurring in the |
|
|
Total Organic Carbon (TOC) |
n/a |
RAA = 1.0 - 2.75 |
n/a |
environment, sewer treatment |
No |
||
RAA ≥ 1 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
plant discharges |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Haloacetic |
LRAA ≤ 60 |
0 |
LRAA = 12.95 - 14.2 |
ppb |
Produced as a byproduct of |
No |
|
Acids |
chlorination at the water |
||||||
Trihalomethanes |
LRAA ≤ 80 |
0 |
LRAA = 23.15 - 37.04 |
ppb |
treatment plant |
No |
|
70 |
n/a |
0.2 |
ppb |
Runoff from herbicide used |
No |
||
on row crops |
|||||||
Radioactive Material |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alpha Radioactivity |
15 |
0 |
2.3 - 4.1 |
pCi/L |
Erosion of natural deposits |
No |
|
Radium 226 & 228 (total) |
5 |
0 |
0.54 - 1.35 |
pCi/L |
Erosion of natural deposits |
No |
|
|
|||||||
Uranium |
20 |
0 |
0.15 - 1.7 |
ppb |
Erosion of natural deposits |
No |
|
Micro Organisms |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Coliform Bacteria |
95% samples free of |
0 |
100% free of coliform |
% |
Human and animal waste, |
|
|
stormwater |
No |
||||||
coliform bacteria |
Zero positive in 1,623 samples |
||||||
|
|
|
plant discharges |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Turbidity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
95% samples < 0.3 |
|
All samples < 0.3 |
|
Particles and sediment |
|
|
Turbidity |
0 |
NTU |
present in natural water |
No |
MCL: Maximum Contaminant Level. The highest level of a contaminant that is allowed in drinking water. MCLs are set as close to the MCLGs as feasible using the best available water treatment technology.
MCLG: Maximum Contaminant Level Goal. The level of a contaminant in drinking water below which there is no known or expected risk to health. MCLGs allow for a margin of safety.
Removal Ratio: A value greater than or equal to one indicates that the required amount of TOC is being removed.
AL: Action Level. The concentration of a contaminant, which if exceeded, triggers treatment or other requirements a water system must follow.
n/a: not applicable
NTU: Nephelometric Turbidity Units, used in the measurement of clarity.
pCi/L: Picocuries per Liter. A picocurie is one
ppm: Parts per Million. A unit used to express the concentration of an element or compound in a liquid. One part per million is equivalent to one teaspoon of salt in 2,000 gallons of water.
ppb: Parts per Billion. A unit used to express the concentration of an element or compound in a liquid. One part per billion is equivalent to one teaspoon of salt in
2 million gallons of water (more than three
RAA: Running Annual Average, the average value over the last 12 months.
LRAA: Locational Running Annual Average, the average value over the last 12 months taken at one specific site.
|
No samples > 1.0 |
No samples > 1.0 |
|
sources and storm |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SECONDARY STANDARDS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contaminant/Parameter |
SMCL |
Range of Detected Results |
Units |
Typical Sources |
Violation? |
||
Chloride |
250 |
43 |
- 196 |
ppm |
Erosion of natural deposits |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sulfate |
250 |
47 |
- 202 |
ppm |
Erosion of natural deposits |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Calcium |
n/a |
33.1 - 77.5 |
ppm |
Erosion of natural deposits |
N/A |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Potassium |
n/a |
2.4 |
- 10.7 |
ppm |
Erosion of natural deposits |
N/A |
|
Magnesium |
n/a |
7.5 |
- 21.7 |
ppm |
Erosion of natural deposits |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sodium |
n/a |
35 |
- 120 |
ppm |
Erosion of natural deposits |
N/A |
|
pH |
6.5 - 8.5 |
7.4 |
- 8.96 |
n/a |
Corrosion control |
N/A |
|
Average = 8.07 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
30 - 70 |
|
Erosion of natural deposits, |
|
||
Iron |
300 |
ppb |
industrial wastes, used in |
N/A |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
water treatment |
|
|
Manganese |
50 |
10 - 60 |
ppb |
Erosion of natural deposits |
N/A |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) |
500 |
90 |
- 757 |
ppm |
Runoff/Erosion of natural |
N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
deposits |
|
|
Zinc |
5,000 |
5.7 - 16 |
ppb |
Erosion of natural deposits, |
N/A |
||
|
|
|
|
|
industrial wastes |
|
|
Hardness of Thornton Water
Hardness is a measure of calcium and magnesium minerals in the water. Water naturally dissolves minerals as it comes in contact with rocks and soil. Hard water is associated with certain problems like mineral
Water Sample Collection - Water Quality staff sample at over 30 sites within the service area each week, year round. For the most recent test results in your area, call the Water Quality Information Line at

Looking Ahead
Thornton continues to make investments in water treatment infrastructure to provide residents with the best possible water. Last fall, the new Thornton Water Treatment Plant came online and utilizes advanced treatment technologies, like ozone oxidation and biological filters to provide enhanced organics removal, including taste and odor compounds. Our staff will continue to focus on fine tuning chemical dosages and other processes to maximize treatment efficiencies in this new water plant. We will also focus on developing wise energy use strategies to help reduce power costs in all facilities.
Thornton continues to work with our northern communities in planning and designing a pipeline that will
deliver high quality, Cache la Poudre River water to Thornton by 2025 and help meet the consumption needs of the city’s growing population. Additionally, Thornton will also work to connect with more local water sources to better prepare for times of drought or rapid community growth.
The EPA has instituted significant changes to the Lead and Copper Rule that will take effect in 2024. Some noteworthy requirements include: forming an inventory of lead service lines, testing schools and day cares, increased public education, and more rigorous public notifications. Thornton will focus significant efforts over the next several years to ensure we remain compliant with all rule changes.
Please share this information with others who drink Thornton water, especially those who may not receive this notice directly, such as people in apartments, nursing homes, schools, and businesses.
For Water Quality Information
W - www.ThorntonCO.gov/waterinfo
E - waterquality@ThorntonCO.gov
P -
2021
Reporte de Calidad de Agua
La ciudad de Thornton se complace en presentar el Informe de Confianza del Consumidor de 2020.
Fuentes de agua de Thornton
La ciudad de Thornton se complace en presentar el Informe de Confianza del Consumidor de 2020, que proporciona una descripción general de las muestras de calidad del agua y los análisis realizados en 2019. Los miembros del personal monitorean el agua potable desde donde comienza a derretirse en la cabecera de la cuenca del río South Platte a lo largo del proceso de tratamiento y sistema de distribución, hasta donde termina en los grifos de los clientes. El Laboratorio de Calidad del Agua de la ciudad analiza muestras
de agua en busca de numerosos contaminantes para garantizar que su agua siempre sea potable. Aunque se redujeron ligeramente
las actividades debido a los cierres y las precauciones relacionadas con la COVID, el personal de calidad del agua aún recolectó más de 2,500 muestras de agua
y llevó a cabo más de 27,000 pruebas analíticas en 2020. Este informe resume las pruebas del año y presenta más información que es importante que conozca. En 2020, no se superaron los estándares estatales o federales de agua potable. Además, Thornton analizó muchos otros contaminantes no regulados y no detectó ningún problema. Póngase en contacto con Calidad del Agua si tiene más preguntas o le gustaría conocer datos más recientes y localizados sobre la calidad del agua.
El agua potable de Thornton inicia como nieve derretida en las montañas.
La ciudad posee derechos de agua en el río South Platte, Clear Creek y e río Cache la Poudre. El agua de South Platte se desvía al norte de Denve y se almacena en una red de lagos de grava antes del tratamiento. La mayor parte del agua del Arroyo Clear se almacena en el Lago Standley, mientras que una menor parte se desvía a los lagos de grava de Thornton. La ciudad actualmente está trabajando arduamente y sigue en tiempo con sus esfuerzos para entregar agua a sus clientes desde el río Cache la Poudre para el año 2025.
SWAP: Informe de Evaluación y Protección de las Fuentes de Agua
En 2002, el Departamento de Salud Pública y Medio Ambiente de Colorado (Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment, CDPHE) realizó una Evaluación de Fuentes de Agua a nivel estatal para todos los proveedores municipales de agua potable. El informe identificó posibles fuentes de contaminantes tales como tanques de almacenamiento de gasolina,
descargas de aguas residuales, drenajes de minas y otras. Estos sitios no necesariamente representan una amenaza, sino que fueron identificados sólo como fuentes potenciales de contaminación. Thornton utiliza esta información par garantizar que todo el monitoreo de rutina incluya estos potenciales contaminantes. Visite el informe en http://www.thorntonco.gov/SWAP.

Información
Es razonable esperar que toda el agua potable, incluyendo el agua embotellada, contenga al menos pequeñas cantidades de algunos contaminantes. La presencia de contaminantes no necesariamente significa que el agua represente un riesgo para la salud. No obstante, algunas personas pueden ser más vulnerables que la población en general a los contaminantes en el agua potable. Las personas con sistemas inmunitarios comprometidos, como las personas con cáncer que reciben quimioterapia, las personas que han recibido trasplantes de órganos, las personas con
los bebés, pueden tener un mayor riesgo de infecciones. Estas personas deben consultar a sus proveedores de servicios de salud respecto al agua potable. Las personas que usan el agua para diálisis pueden comunicarse con el Laboratorio de Calidad del Agua de la ciudad para recibir notificaciones anticipadas de los cambios en el tratamiento.
Para garantizar que el agua del grifo pueda beberse de manera segura, el CDPHE emite normas que limitan la cantidad de ciertos contaminantes en el agua distribuida por sistemas públicos de agua. Las normas de la Administración de Alimentos y Medicamentos establecen límites a los contaminantes en el agua embotellada, que debe brindar la misma protección a la salud pública.
Las fuentes de agua potable (tanto el agua del grifo como el agua embotellada) tales como ríos, lagos y arroyos, contienen minerales naturales, incluyendo materiales radioactivos, que no se eliminan por completo en las plantas de tratamiento de agua y que pueden representar un riesgo para la salud humana si están presentes a una concentración superior a los niveles seguros establecidos por la EPA. Los contaminantes que pueden estar presentes en las fuentes de agua incluyen:
-
Contaminantes microbianos, como virus y bacterias que pueden provenir de plantas de tratamiento de aguas negras, sistemas sépticos, operaciones ganaderas y vida silvestre. Las directrices de EPA/CDC sobre medios apropiados para disminuir el riesgo de infección por Cryptosporidium y otros contaminantes microbianos están disponibles en la línea directa de agua potable segura
(1-800-426-4791). Es importante señalar que,
de acuerdo con la EPA, el CDC y otras agencias sanitarias, no existen evidencias de que el coronavirusCOVID-19 actual pueda transmitirse en el agua potable. - Contaminantes inorgánicos, tales como sales y metales, que pueden presentarse de manera natural o ser resultado de descargas de
Sanitaria
aguas pluviales urbanas, descargas de aguas residuales industriales o residenciales, producción de petróleo y gas, minería o agricultura.
- El plomo, si está presente en niveles elevados, puede causar problemas graves de salud, especialmente a mujeres embarazadas y niños pequeños. El plomo en el agua potable proviene principalmente de materiales y componentes de las tuberías de servicio y de las tuberías propias de las viviendas. Thornton es responsable de proporcionar agua potable de alta calidad, pero no puede controlar la variedad de materiales utilizados en los materiales de plomería. Cuando su agua ha permanecido estancada por varias horas, puede minimizar la potencial exposición al plomo si deja correr el agua de 30 segundos a 2 minutos antes de utilizarla para beber o cocinar.
Thornton no permite la instalación de tuberías de plomo, y los niveles elevados de plomo no son un problema en la ciudad. Eso se confirmó cuando la ciudad hizo dos rondas de pruebas en 2020. Sin embargo, quizá usted desee realizar pruebas en su agua si le preocupa la posible presencia de plomo. Sin embargo, quizá usted desee realizar pruebas en su agua si le preocupa la posible presencia de plomo. Hay información disponible sobre el plomo en el agua potable, los métodos de prueba, y las medidas que puede tomar para minimizar la exposición en la línea de ayuda para agua potable segura al
- Pesticidas y herbicidas que pueden provenir de una variedad de fuentes, como la agricultura, las descargas de aguas pluviales urbanas y los usos residenciales.
- Contaminantes químicos orgánicos, entre ellos las sustancias orgánicas sintéticas y volátiles, que son subproductos de procesos industriales y de la producción de petróleo, y que también pueden provenir de gasolineras, descargas de aguas pluviales urbanas y sistemas sépticos.
- Contaminantes radioactivos, que pueden presentarse de manera natural o ser resultado de actividades de producción de petróleo y gas y de minería.
Para obtener más información sobre los contaminantes y sus posibles efectos sobre la salud, llame a la línea de ayuda para agua potable segura de la EPA al

Agua de Thornton |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ninguna norma estatal o federal referente al agua potable fue rebasada en 2020. |
|
|
|
|||||
NORMAS PRIMARIAS |
|
|
Rango de resultados |
|
|
|
||
Contaminante |
MCL |
MCLG |
detectados |
Unidades |
Fuentes típicas |
¿Violación? |
||
|
|
|
( í |
á ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Descargas de refinerías de |
|
|
Antimonio |
6 |
n.a. |
|
0.44 |
ppb |
petróleo, retardadores de |
No |
|
|
fuego, cerámica, electrónica, |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
soldadura |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Erosión de depósitos |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
naturales, escorrentías de |
|
|
Arsénico |
50 |
n.a. |
|
1.2 |
ppb |
huertos, desechos de |
No |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
producción de vidrio y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
aparatos electrónicos |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Descarga de desechos de |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
perforación petrolera y de |
|
|
Bario |
2,000 |
2,000 |
41 - 51 |
ppb |
refinerías |
No |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
de metal, erosión de |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
depósitos naturales |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Descarga de acerías, |
|
|
Cromo |
100 |
100 |
1.1 - 1.5 |
ppb |
plantas de celulosa y |
No |
||
cromado, erosión de |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
depósitos naturales |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Erosión de depósitos |
|
|
Níquel |
100 |
n.a. |
1.3 - 5.2 |
ppb |
naturales, descarga |
No |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
de fábricas de metal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Descargas de refinerías de |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
petróleo, vidrio y metal, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
erosión de depósitos |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
naturales, descargas de |
|
|
Selenio |
50 |
50 |
1.3 - 1.7 |
ppb |
minas y |
No |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
fabricantes de sustancias |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
químicas, escorrentías de |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ranchos ganaderos (aditivo |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
de pastura) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Erosión de depósitos |
|
|
Fluoruro |
4 |
4 |
0.37 - 1.22 |
ppm |
naturales; Thornton no añade |
No |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
fluoruro al agua |
|
|
Nitrato |
10 |
n.a. |
0.1 - 1.61 |
ppm |
Fertilizantes, tanques |
No |
||
sépticos, descargas de |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
plantas de aguas negras, |
|
|
Nitrito |
1 |
n.a. |
|
0.05 |
ppm |
depósitos naturales |
No |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
AL > 15 |
|
0.5 - 38 |
|
Tuberías caseras, |
|
||
Plomo |
0 |
90% de las muestras ≤ 2.4 - |
ppb |
fabricación de baterías, |
|
|||
90% de las muestras ≤ |
No |
|||||||
|
2.5 |
erosión de depósitos |
||||||
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
2 sitios > 15 |
|
naturales |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
AL > 1,300 |
|
9.8 - 1,430 |
|
Tuberías caseras, |
|
||
Cobre |
|
90% de las muestras ≤ 720 - |
ppb |
preservadores de madera, |
|
|||
90% de las muestras ≤ |
1,300 |
No |
||||||
|
969 |
erosión de depósitos |
||||||
|
1,300 |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
3 sitios > 1,300 |
|
naturales |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Desinfectantes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cloro |
RAA ≤ 4 |
4 |
1.89 - 2.79 |
ppm |
Añadido en el proceso de |
No |
||
(en forma de cloramina) |
RAA = 2.46 |
tratamiento de agua |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|||||
Sustancias químicas orgánicas |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Se presenta de manera |
|
|
Carbono Orgánico Total |
Tasa de depuración |
|
|
|
|
natural en el medio |
|
|
n.a. |
RAA = 1.0 - 2.75 |
n.a. |
ambiente, descargas de |
No |
||||
(COT) |
RAA ≥1 |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
plantas de tratamiento de |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
aguas negras |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ácidos |
LRAA ≤ 60 |
0 |
LRAA = 12.95 - 14.2 |
ppb |
Producidos como |
No |
||
haloacéticos |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
subproducto de la aplicación |
|
|
Trihalometanos |
LRAA ≤ 80 |
0 |
LRAA = 23.15 - 37.04 |
ppb |
de cloro en la planta de |
|
||
tratamiento de agua |
No |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70 |
n.a. |
|
0.2 |
ppb |
Escorrentías de herbicidas |
No |
||
|
usados en cultivos en hilera |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Definiciones
MCL: Nivel máximo de contaminante. El nivel más alto de un contaminante que se permite en agua potable. Los MCL se establecen tan cerca de los MCLG como es factible utilizando la mejor tecnología disponible para tratamiento de agua.
MCLG: Nivel máximo permisible de contaminante. El nivel de un contaminante en agua potable bajo el cual no existen riesgos conocidos o esperados para la salud. Los MCLG ofrecen un mayor margen de seguridad.
Tasa de depuración: Un valor mayor o igual a uno indica que se está depurando la cantidad requerida de COT.
AL: Nivel de acción: La concentración de un contaminante que, si se excede, desencadena tratamientos u otros requisitos que un sistema de agua debe cumplir.
n.a.: no aplicable
NTU :Unidades nefelométricas de
turbidez, utilizadas para medir la claridad. pCi/L: PicoCuries por litro. Un picoCurie es un diezmilésimo de la energía emitida por un gramo de radio.
ppm: Partes por millón. Una unidad utilizada para expresar la concentración de un elemento o compuesto en un líquido. Una parte por millón equivale a una cucharadita de sal en 2,000 galones de agua.
ppb: Partes por mil millones. Una unidad utilizada para expresar la concentración de un elemento o compuesto en un líquido. Una parte por mil millones equivale a una cucharadita de sal en dos millones de galones de agua (más de tres piscinas olímpicas).
RAA: Promedio anual corriente, el valor promedio a lo largo de los últimos 12 meses.
LRAA: Promedio anual corriente por localidad, el valor promedio a lo largo de los últimos 12 meses en un sitio específico.
Materiales radioactivos |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Radioactividad alfa |
15 |
0 |
2.3 - 4.1 |
pCi/L |
Erosión de depósitos naturale |
No |
|
Radio 226 y 228 (total) |
5 |
0 |
0.54 - 1.35 |
pCi/L |
Erosión de depósitos naturale |
No |
|
Uranio |
20 |
0 |
0.15 - 1.7 |
ppb |
Erosión de depósitos naturale |
No |
|
Microorganismos |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
95% de las muestras |
|
100% sin coliformes |
|
Desechos humanos y |
|
|
Bacterias coliformes |
|
|
animales, descargas de |
|
|||
no presentan bacterias |
0 |
Cero muestras positivas de |
% |
No |
|||
aguas pluviales, descargas |
|||||||
|
coliformes |
|
1,623 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
de plantas de aguas negras |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Turbidez |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
95% de las muestras |
|
|
|
Partículas y sedimentos |
|
|
|
|
Todas las muestras <0.3 |
|
presentes en fuentes |
|
||
Turbidez |
<0.3 |
0 |
NTU |
No |
|||
Ninguna muestra >1.0 |
naturales de agua y en |
||||||
|
Ninguna muestra >1.0 |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
descargas pluviales |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NORMAS SECUNDARIAS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contaminante/Parámetro |
SMCL |
Rango de resultados detectados |
Unidades |
Fuentes típicas |
¿Violación? |
||
Cloruro |
250 |
|
43 - 196 |
ppm |
Erosión de depósitos |
N.A. |
|
|
naturales |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Sulfato |
250 |
|
47 - 202 |
ppm |
Erosión de depósitos |
N.A. |
|
|
naturales |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Calcio |
n.a. |
|
33.1 - 77.5 |
ppm |
Erosión de depósitos |
N.A. |
|
|
naturales |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Potasio |
n.a. |
|
2.4 - 10.7 |
ppm |
Erosión de depósitos |
N.A. |
|
|
naturales |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Magnesio |
n.a. |
|
7.5 - 21.7 |
ppm |
Erosión de depósitos |
N.A. |
|
|
naturales |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Sodio |
n.a. |
|
35 - 120 |
ppm |
Erosión de depósitos |
N.A. |
|
|
naturales |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
pH |
6.5 - 8.5 |
|
7.4 - 8.96 |
n.a. |
Control de corrosión |
N.A. |
|
|
Promedio = 8.07 |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Erosión de depósitos |
|
|
Hierro |
300 |
|
30 - 70 |
ppb |
naturales, desechos |
N.A. |
|
|
industriales, uso en |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
tratamiento de agua |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Manganeso |
50 |
|
10 - 60 |
ppb |
Erosión de depósitos |
N.A. |
|
|
naturales |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Sólidos disueltos totales |
500 |
|
90 - 757 |
ppm |
Escorrentía/Erosión de |
N.A. |
|
(TDS) |
|
depósitos naturales |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
5.7 - 16 |
|
Erosión de depósitos |
|
|
Zinc |
5,000 |
|
ppb |
naturales, desechos |
N.A. |
||
|
|
|
|
|
industriales |
|
|
Dureza del agua de Thornton
La dureza es una medida de los minerales de calcio y magnesio en el agua. El agua disuelve minerales de manera natural cuando entra en contacto con las rocas y la tierra. El agua dura se relaciona con ciertos problemas como la acumulación de minerales en vajilla, accesorios de plomería y tuberías. La dureza del agua de Thornton puede variar mucho según la época del año y la ubicación en la ciudad. Durante 2019 la dureza varió entre 88 mg/L y 288 mg/L. Estos valores son típicos de los sistemas de agua en el oeste de Estados Unidos, pero están ligeramente elevados respecto al año anterior debido a las condiciones de sequía en 2020. Comuníquese con la División de Calidad del Agua si desea conocer la dureza en su residencia o negocio en particular.
Toma de muestras de agua - El personal de Calidad del Agua toma muestras en más de 30 sitios dentro del área de servicio cada semana, durante todo el año. Para ver los resultados más recientes de las pruebas en su zona, llame a la línea de información sobre calidad del agua al

Visión a futuro
Thornton continúa invirtiendo en infraestructura de tratamiento del agua para brindarle la mejor agua posible a los residentes. En otoño pasado inició sus actividades la nueva Planta de Tratamiento de Agua de Thornton, que utiliza tecnologías avanzadas de tratamiento, como oxidación con ozono y filtros biológicos, para lograr una mejor eliminación de residuos orgánicos, incluyendo compuestos con sabor
y olor. Durante el año, el personal seguirá concentrándose en afinar la dosificación de sustancias químicas y otros procesos para maximizar la eficiencia del tratamiento en esta nueva planta de agua. El personal también se concentrará en desarrollar estrategias de bajo consumo de energía para ayudar a reducir los costos de energía en todas las instalaciones.
La ciudad continúa trabajando con nuestras comunidades del norte en la planificación y el diseño de
un acueducto que llevará agua de alta calidad del río Cache la Poudre a Thornton para 2025 y ayudará
a satisfacer las necesidades de consumo de la creciente población de la ciudad. Además, la ciudad trabajará en conectarse a más fuentes de agua de la localidad para prepararse mejor para las épocas de sequía y para el rápido crecimiento de la comunidad.
La EPA implementó cambios importantes a la Regla sobre Plomo y Cobre, que entrarán en vigor en 2024. Algunos requisitos notables son: hacer un inventario de las tuberías de servicio de plomo, hacer pruebas en escuelas y guarderías, aumentar la educación pública y requisitos más estrictos de notificación pública. Thornton hará importantes esfuerzos en los próximos años para asegurarnos de cumplir con todos los cambios en las reglas.
El personal de Calidad del Agua toma muestras en más de 30 sitios dentro del área de servicio cada semana, durante todo el año. Para ver los resultados más recientes de las pruebas en su zona, llame a la línea de información sobre calidad del agua al
Visite www.thorntonco.go/waterinfo waterquality@ThorntonCO.gov
o llame al
Contaminants
City of Thornton
EWG's drinking water quality report shows results of tests conducted by the water utility and provided to the Environmental Working Group by the Colorado Department of Public Health & Environment, as well as information from the U.S. EPA Enforcement and Compliance History database (ECHO). For the latest quarter assessed by the U.S. EPA (January 2019 - March 2019), tap water provided by this water utility was in compliance with federal health-based drinking water standards.
Utility details
- Serves: 136977
- Data available: 2012-2017
- Data Source: Surface water
- Total: 22
Contaminants That Exceed Guidelines
- Bromate
- Bromodichloromethane
- Bromoform
- Chlorate
- Chloroform
- Chromium (hexavalent)
- Dibromoacetic acid
- Dibromochloromethane
- Dichloroacetic acid
- Haloacetic acids (HAA5)†
- Nitrate
- Nitrate and nitrite
- Radium
- combined (-226 & -228)
- Total trihalomethanes (TTHMs)†
- Trichloroacetic acid
- Uranium
Other Detected Contaminants
- Barium
- Chromium (total)
- Fluoride
- Molybdenum
- Nitrite
- Strontium
Reminder
Always take extra precautions, the water may be safe to drink when it leaves the sewage treatment plant but it may pick up pollutants during its way to your tap. We advise that you ask locals or hotel staff about the water quality. Also, note that different cities have different water mineral contents.
Sources and Resources
Sources Cited
Additional Resources
Thornton Tap Water
As if the questions about the quality of your tap water in Thornton are not enough, now it seems that you may also be concerned about the quality of the water that your children are drinking. The problem is that there have been many cases where the water delivered to our homes contains measurable levels of contaminants that can cause a variety of health problems. And there are many cases where these contaminants have been found in the blood samples taken from one or more residents. Many of the contaminants that can be found in the water are categorized as being cancer-causing.
This means that if you or one of your family members become ill because of the water you or your loved ones are drinking, then that individual is responsible for that cost. Yes, it is true that in most areas, the water treatment facilities are pretty effective at removing most of the various contaminants that find their way into the system. However, it is still essential to understand that the water can get back into the distribution system or even find its way back into the tap water of many areas. That is why each homeowner needs to understand just how and why their water is being treated.
If you are looking for a better answer to the question “How clean is Thornton Colorado tap water?” then it may be time to consider installing a home water purifier of some sort. These units use various methods to remove various kinds of contaminants from the tap water, including chlorine, volatile organic compounds, prescription drugs, and a wide variety of different heavy metals. Purifies of this type can be found in various price ranges. Still, they all use similar methods to ensure that the end product is high quality and pure.
Thornton Drinking Water
Thornton, Colorado, drinking water, which certainly sounds like a mouthful, yet when you see the location and what it offers, you realize that it is not a mouthful. This beautiful little mountain community is nestled in between three other mountains on the Colorado River Basin in the northeast corner of Colorado. That’s the beauty of this place-it’s perfect for mountain people and those who enjoy the outdoors. Still, it also has some luxurious amenities for those interested in a bit of luxury. There are three hotels in this area. The Heritage Lodge is a three-star deluxe facility.
For less than the price of a taxi ride, you can get yourself a room at this hotel and be treated to a lovely, quiet night in bed, a nice hot shower, and a comfortable bed. Suppose you want something a bit less expensive. In that case, you can try the neighboring Mountain Shadows Lodge, which is very basic but clean and reasonably priced. Then of course, if you are interested in a bit more, you can try the Waterworks Lodge, which has a nice restaurant and pool facilities, as well as Jacuzzi tubs and steam rooms.
As you can see, this area has a little bit to offer with everything needed to pamper yourself. There are many excellent ski resorts in this area, which makes it all the more interesting. The beauty of living in this area is that you don’t have to give up any of your comforts to enjoy a lovely day in the mountains. You can get the peace you need and still enjoy the great amenities that the area offers. It seems that there is another sight of beauty everywhere you turn, which is enough to make anyone happy.
Thornton Water Quality
If you live in the City of Thornton, Colorado, you will realize that it has excellent water quality. It has been getting exceptional precipitation for many decades. The city is known as a valley town with lots of recreation opportunities. You will enjoy the recreational opportunities and see all of the beautiful sights this beautiful town has to offer. Suppose you own a home in the City of Thornton. In that case, it is essential that you take care of your water quality there, and the best way to do this is by having a quality water filter. Having a quality filter will ensure that you are taking excellent care of your water. You will be doing your part to sustain a healthy environment.
There are many benefits to having a quality water filter in your home. Some of these benefits include saving money and helping to maintain a healthy lifestyle. People in western Colorado have a long history of enjoyment with their water. There is no question that you will enjoy your water even more, when you use a filter for it. Filters can help remove chemicals and minerals that can harm your health. Water is the most critical fluid in your body. A good water filter can ensure that you always get the purest water possible.
A water filter will also extend the life of your water heater. Hot water will increase your house’s temperature, which can cause problems if your heater does not have adequate water flow to prevent the increase in temperature. You can save a tremendous amount of money on your home heating bill with a filter on your faucet, and these savings will be passed along to you! The importance of taking care of your water quality cannot be stressed enough. If you don’t filter your water, you could be putting your family at risk. There is no reason why you should ever have to spend money on a water heater when you can take care of the problem yourself with a filter.
Thornton Water Treatment
Suppose you live in the community of Thornton, Colorado. In that case, you know that there is a lot of good that can come out of having your town’s water treatment facilities serviced by one of the many excellent water treatment companies in the area. However, while most towns have several to choose from, it can be difficult knowing which is best for you and your family. Many towns and cities throughout the nation are suffering from the same problems that have plagued other towns across the nation; dioxins in drinking water, for example. These dioxins are linked to cancer, but most people don’t even realize that they may have been exposed to them until something becomes wrong.
For this reason, every home must have a quality water treatment system in place to keep yourself and your family safe. There are several different options available when it comes to choosing a water filtration system for your home. Depending on where you live, the types of contaminants you might be exposed to will be different. For example, if you live in a heavily wooded area or if you drink a lot of, then having a filter on all of your drinking water is a great idea. You can even choose to have a filter installed in your showerheads to eliminate the impurities in the steam.
The water filter system you choose should have specific features to make sure that you get the most benefit from the purchase. For example, some filters will offer you the convenience of changing out the cartridge filters as needed so that you can avoid having to do that a lot. Others will offer you the option to have a self-cleaning filter system if you forget to change the cartridge before you shower each day. Whatever type of filter system you decide upon, remember that your health is essential and that you can never be too safe. Take the time to choose the right filter for your home, and you will be glad that you took the time to protect yourself and your family.
Thornton Water Utility
When you live in a home in the mountains, you need a good water utility company with dependable service in your area. But it can be a challenge when you are looking for affordable and reliable quality and provides quality service. That’s why it’s a good idea to research what a good Colorado water utility looks like before you commit. You might be surprised by what you find out.
The first place to start when searching is the city of Thornton. This is the largest city in the area and provides access to both the South Platte and North Denver Canal and the Colorado River. It is home to many businesses, such as Von Grumman’s Commercial Water Park and The Denver Art Museum. The homes and commercial buildings are also top-notch. There is plenty to do in the way of recreational opportunities and events, as well.
If you’re looking for a water utility company in the mountains with the reputation you want, this area of Colorado has several companies to choose from. You won’t have any trouble finding a service that suits your needs and your budget. Just make sure that you get a good experience. And, keep in mind that your home is an investment, so take care of it.
Thornton Water Treatment Plant
The water treatment plant in Thornton, Colorado, is an important one. It serves a town of about 4.5 million people, and it is the giant water treatment plant in Colorado. Because of this large amount of responsibility and importance, it is essential to know some of its histories. When a local creek in the mountains of Colorado floods, this same creek ends up going through the water treatment plant. Over the years, this stream has caused problems with the water treatment facility.
To start with, it was built in 1931. It was built primarily due to a shortage of water in the area, and the plant itself was also built in an attempt to conserve water. These problems caused problems for many years because the water that was allowed to flow through the plant would end up running down to the creek before it could make it to its destination. This was because the water treatment plant was not designed to handle the amount of water allowed to get through.
More recently, in 2021, the city of Thornton was required to remove 8.2 million gallons of contaminated water from the river. This contamination came from the runoff that happens when there is heavy rainfall. Since this happened regularly, it had caused the water to become over-stocked. It was consequently being filtered too much by this facility. It also had the wrong type of equipment to deal with the situation. It caused even more problems than initially anticipated.
Water in Thornton
The water in Thornton, Colorado, can be a little bit pricey, depending on what you want to do with it. There are plenty of water companies in the area, and they all have different methods for billing and receiving payment. Some standard service charges can apply to water companies, depending on how long the water is supposed to last. This information is excellent for anyone trying to find a company near them. It will allow them to see whether the money they are being charged will make their water much more cost-effective.
Some water companies offer customers discounts if the water they are delivering is clean and of good quality. It helps to keep bacteria from ruining the water, and the chemicals used to treat it are essential to our health. Sometimes customers have to pay an additional fee if they choose a water company that offers this type of service. Certain types of water cannot be treated and sent to a customer’s home. These water sources include naturally filtered spring water and even springs that have been purified through means that are not as clean as they would be if they were filtered at home. If a customer wants to know whether their water supply is one of these cleaner types, they should ask their water companies about it. They may tell them what kinds of water can be safely delivered and what kind of filtration systems the company has to clean the water.
Some companies also charge extra for delivery and pickup. This can become a hassle if the customer only uses a portion of the water in their water tank, so it is beneficial to get water delivered as close to the customer as possible. This allows for the water to be better circulated and allows water companies to turn off faucets as needed to avoid having pipes get blocked. Some businesses deliver water to customers’ homes, while others offer the water to residential customers and businesses. This is especially helpful for businesses with outdoor grills and a constant supply of clean water.
Thornton Drinking Water Standards
Amid a heated political debate over clean air and clean water, the Thornton Colorado drinking water standards were recently loosened. The Denver Post published an article stating that the standards had been relaxed to allow for an increase in the percentage of “active” versus “passive” carbon filters. Currently, the standards require at least a 3.5% active carbon filter, but the new standard will require up to five. Of course, this means more money for large corporations and less for you, the consumer. However, there is a good reason why the state government and city officials made this change; it was done in response to the growing threat of home purifiers. Many of the large residential water purifiers on the market do not meet active carbon filter standards. It was found that most home filter systems only account for about 10% of the total carbon in the water.
Suppose you have been shopping for a home water filter system. In that case, you may already know that your choice of purification method can impact the overall purity of your water. Active carbon filter removes chlorine and other chemicals while at the same time keeping the healthy minerals in the water like calcium and magnesium. Therefore, you are getting the maximum benefit from your active carbon filter; however, if you choose a reverse osmosis system or distillation method, your mineral content will be reduced. The taste will become bland and lifeless.
Hopefully, this news will help homeowners who are concerned about the healthfulness of their drinking water. If you want to shop for a home water filter system, make sure you are buying certified performance data and performance reports. It would be best if you also remembered that the standards for water in Colorado have remained consistent for years. If your area’s standards have changed, you need to check your local water authority first.
Thornton Water System
While many areas of the country are experiencing problems with their water systems, some Denver Area residents have found that the quality of their supplied water is outstanding. The city of Denver installed a new water system that was purposely designed to produce the most efficient results possible. This means that every water pipe in the home is connected by more than one water transport point. If there is a problem with a pipe, it can be traced back to the appropriate point and fixed quickly without disruption of the home’s plumbing system. If you want to know if your water is up to par with other Denver area residents, you can test it yourself at one of several accredited testing centers. These centers give customers the ability to take a sample of their drinking water and then test for quality. When you take this initial step, you will know whether or not your entire home’s water source is up to the standards set by the Department of Health.
In addition to this quality testing service, your local phone number will be available for customer service if you experience a problem with your current water system. This means that if you experience anything from a low reading to unusual smells, you will be able to get in touch with someone who can help. The Department of Health has set several specific criteria for the acceptable standard level for home water. This is especially important in terms of children since very young children and those with existing medical conditions should never drink from any source that is considered to be unsafe. Since most people probably aren’t aware of the various contaminants present in the public’s supply, the department of health recommends testing these things monthly. This way, individuals will be prepared to make the necessary adjustments if problems with their water system arise.
Having a good quality water supply is extremely important, and the people of Thornton have taken great care to ensure that every home is adequately serviced. To find out more about whether or not your Denver water system is up to standard, contact a company that offers quality water only testing. From there, you can discover whether or not the water in your area is healthy and pure. If it is, then you can enjoy delicious water from your kitchen faucet instead of waiting for it to run cold in your refrigerator.